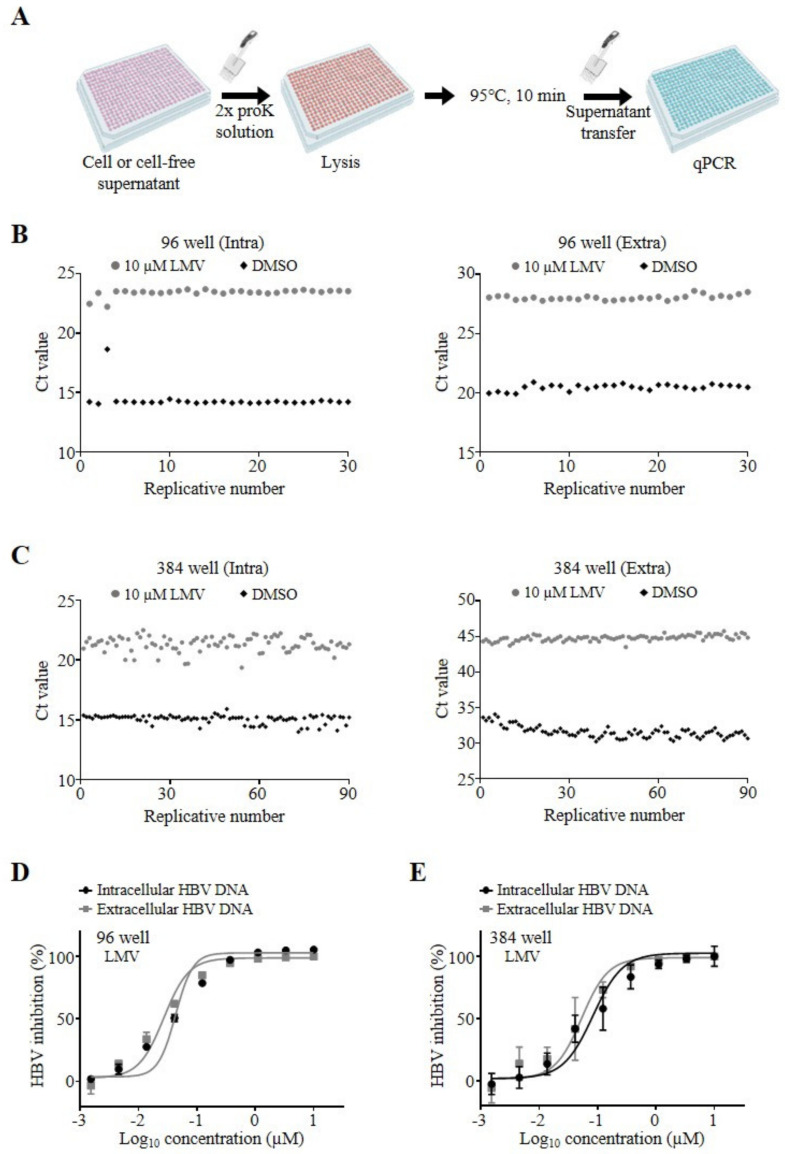
Figure 3.
Assay validation in microtiter plates. (A) Schematic workflow of column-free DNA preparation in microtiter plates. HepAD38 cells were prepared and treated with LMV, as described above. Cells or cell-free supernatants in 96- or 384-well microtiter plates were lysed and subjected to the same plate format for qPCR analysis. HepAD38 cells were plated in 96- or 384-well microtiter plates at 1 × 105 cells/well (B) and 2.5 × 104 cells/well (C), respectively. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA was prepared from cells (Intra, left) or supernatants (Extra, right) using the column-free method and analyzed by qPCR. Replicative numbers and Ct values of controls treated with DMSO (black diamonds) or 10 µM LMV (gray circles) are depicted as scatter plots on the x- and y-axes, respectively. (D,E) Dose–response curve analysis of intra- (black circles) and extracellular (gray squares) HBV DNA by LMV treatment of HepAD38 cells in 96- (D) or 384-well (E) plates. HBV DNA was analyzed by qPCR and normalized as described above. The concentrations of compounds in log scale and percent HBV inhibition are depicted on the x- and y-axes, respectively. Representative data of two independent experiments are shown as mean ± standard deviation (s.d.).