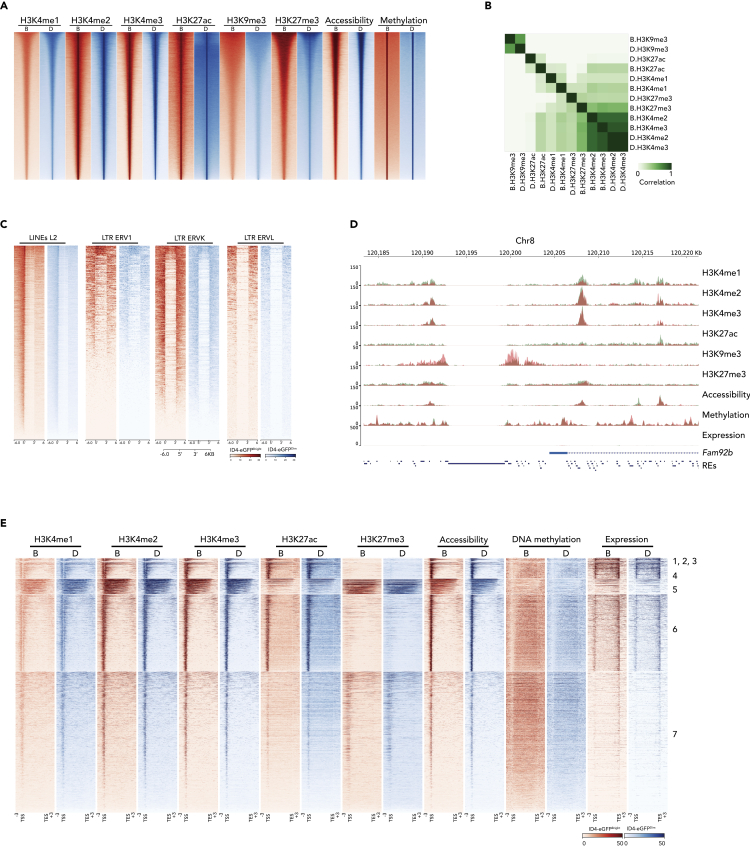
Figure 2.
Epigenetic Profiling of Genic Regions in ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim Spermatogonial Subpopulations
(A) A heatmap shows peaks of histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me2, H3K4me3, H3K9me1, H3K27ac, and H3K27me3) deduced by ChIP-seq, chromatin accessibility deduced by ATAC-seq, and DNA methylation deduced by MeDIP-seq in ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia. Red color indicates reads from ID4-eGFPBright B cells; blue color indicates reads from ID4-eGFPDim D cells.
(B) A heatmap depicts correlations among individual histone modification patterns in ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia.
(C) Heatmaps of H3K9me3 deposition in four types of repeats—LINEs(L2) and LTRs (ERV1, ERVK, ERVL) in ID4-eGFPBright (red) and ID4-eGFPDim (blue) spermatogonia.
(D) A genome browser snapshot showing sequencing reads of six histone modifications, chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation, and transcript expression in ID4-eGFPBright (coral colored tracks) and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia (green colored tracks). The location of a gene that is expressed in both ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia (Fam92b) as well as that of repeat elements is shown at the bottom of this browser image.
(E) Epigenetic profiles within genic regions (TSS – TES + 3 kb upstream and 3 kb downstream) of all mouse Refseq annotated genes (n = 24,012) in ID4-eGFPBright (red tracks, B) and ID4-eGFPDim (blue tracks, D) spermatogonia together with corresponding transcript expression tracks. K-means clustering revealed seven distinct epigenetic profiles, including three that are too small to visually resolve (1–3). The order of genes represented in these tracks is shown in Table S2.