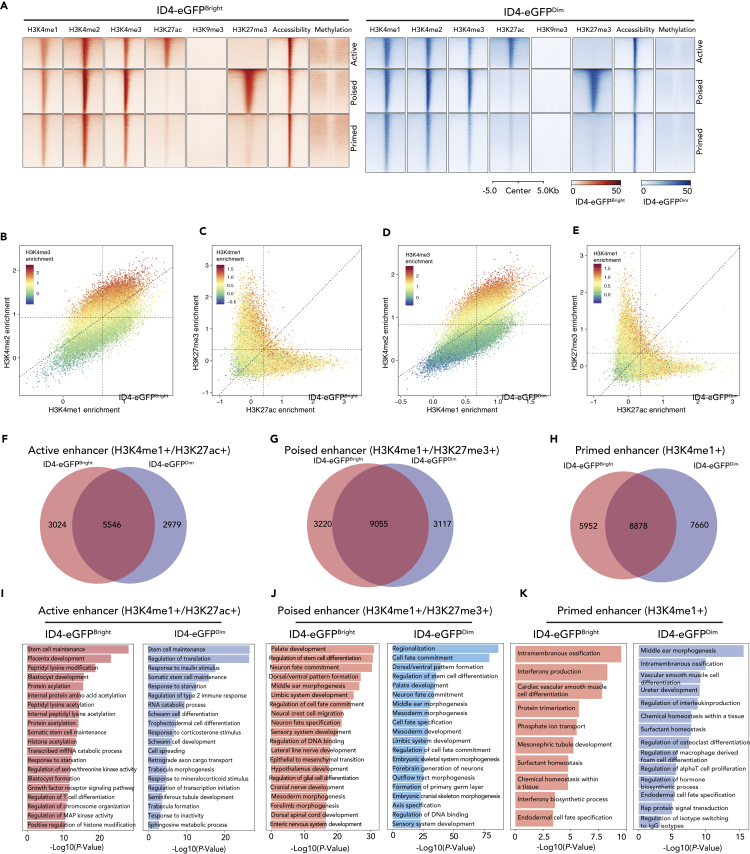
Figure 4.
Epigenetic Profiling at Enhancers in ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim Spermatogonia
(A) Heatmaps show profiles of each set of histone modification, chromatin accessibility, and DNA methylation peaks at sites of intergenic enhancers in ID4-eGFPBright (red) and ID4-eGFPDim (blue) spermatogonia. Peak profiles are shown for active, poised, and primed enhancers in each spermatogonial subtype. Genomic coordinates of enhancers shown in this figure are listed in Table S3.
(B–E) Scatterplots showing positive or negative combinatorial enrichment of different histone modifications at enhancers. Dashed lines indicate the minimum threshold value indicative of enrichment within each bimodal distribution. Each dot is 1 enhancer. (B) Enrichment of the H3K4me3 modification correlates positively with enrichment of the H3K4me2 and H3K4me1 modifications. (C) Enrichment of the H3K4me1 modification correlates positively with enrichment of either the H3K27me3 or the H3K27ac modifications, but enrichment of the H3K27me3 modification correlates negatively with enrichment of the H3K27ac modification, and vice versa. (D) Enrichment of the H3K4me3 modification correlates positively with enrichment of either the H3K27me3 or the H3K27ac modifications, but enrichment of the H3K27me3 modification correlates negatively with enrichment of the H3K27ac modification, and vice versa.
(F–H) Venn diagrams show proportions of active (F), poised (G), and primed (H) enhancers unique to ID4-eGFPBright spermatogonia, common to both ID4-eGFPBright and ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia, or unique to ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia.
(I–K) GREAT GO analysis of functions encoded by genes associated with active (I), poised (J), or primed (K) enhancers in ID4-eGFPBright or ID4-eGFPDim spermatogonia.