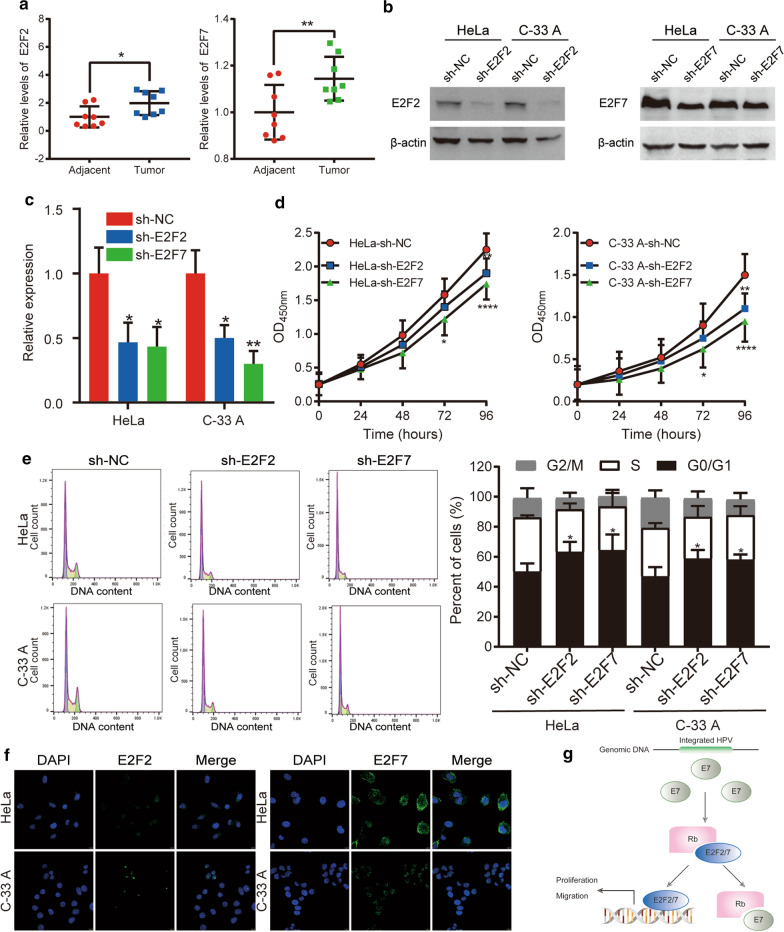
Fig. 7.
Knockdown of E2F2 and E2F7 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest. a E2F2 and E2F7 expression was increased in cervical cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. b, c Evaluation of E2F2 and E2F7 knockdown efficiency in HeLa and C-33 A cells by Western blot and RT-PCR. d Immunofluorescent localization of E2F2 and E2F7 in HeLa and C-33 A cells. e Cell proliferation was determined in HeLa and C-33 A cells by CCK-8 assay. f Cell cycle analysis of HeLa and C-33 A cells by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). g Proposed model for E2F2- and E2F7-induced proliferation and migration in cervical cancer. The human papillomavirus E7 oncogene, which abrogates RB protein function, released “freed E2F2/7”, and activates E2F-regulated genes of proliferation and migration. All experiments were performed in triplicate. *p-value t-test < 0.05; **p-value t-test < 0.01; ****p-value t-test < 0.0001 versus NC group