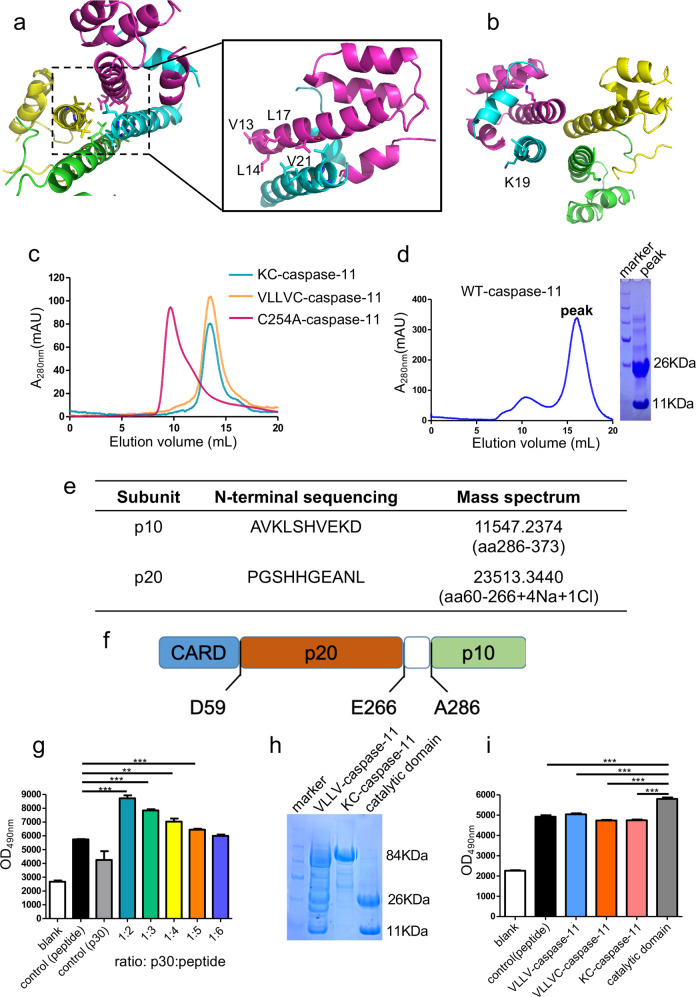
Fig. 3. Mutations abolish the aggregation of caspase-11 CARD and prohibit the self-cleavage of caspase-11.
a The four hydrophobic amino acids on H1–2, V13, L14, L17, and V21, are indicated as sticks. b The basic amino acid K19 resides in the middle of H1–2 and is indicated as a stick. c Gel-filtration chromatography of E. coli-expressed C254A-caspase-11, K19E-caspase-11, and VLLV-caspase-11 (both in K19E-caspase-11 and VLLV-caspase-11 are on the C254A background). d E. coli-expressed wild-type mature caspase-11 protein (left panel), the corresponding SDS-PAGE gel is shown on the right. e Initial ten amino acids detected by N-terminal sequencing of the two bands in d transferred to a PVDF membrane and mass spectrum detecting the molecular weight of the two bands in d. f Diagram of caspase-11 and the self-cleavage sites. g Proteolytic activity assay on the predicted caspase-11 catalytic domain. GSDMD cleavage reporter was mixed with different amounts of the predicted caspase-11 catalytic domain. The initial concentration of predicted caspase-11-catalytic domain is 1 μM. All data shown are representative of at least three independent repeats. h VLLV mutation reduces self-cleavage of full-length caspase-11 revealed by SDS-PAGE analysis. i Synthetic DABYL-GQLSLLSDGID-glu (edans) (GSDMD cleavage reporter) was used as the substrate of mature caspase-11 and the concentration ratio of caspase-11 proteins to the reporter is 1 : 5. All data shown are representative of at least three independent repeats.