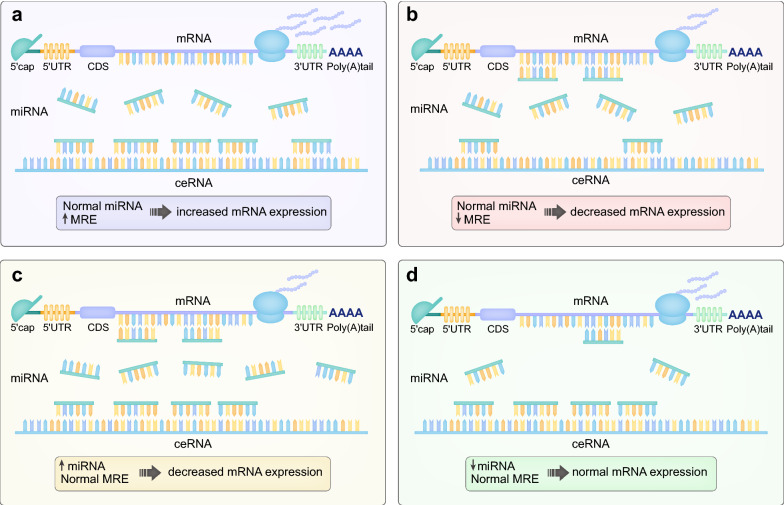
Fig. 3.
The mechanisms of ceRNA regulatory networks. CeRNAs and mRNAs share a pool of miRNAs, and the competition for miRNAs leads to a dynamic regulation of the expression level of mRNAs. a ceRNA with up-regulated miRNA response elements (MREs) can “absorb” more miRNAs, thus the mRNA expression is increased. b When the MRE is down-regulated, miRNAs tend to bind with and silence mRNAs, leading to a decrease in mRNA expression. c miRNA up-regulation exceeds the “sponge effect” of ceRNAs, and mRNA expression is inhibited by excessive miRNAs. d miRNA level is decreased, and mRNA can be expressed normally. In addition, the subtle regulation of one certain mRNA can be achieved by the interactions of multiple miRNAs and ceRNAs