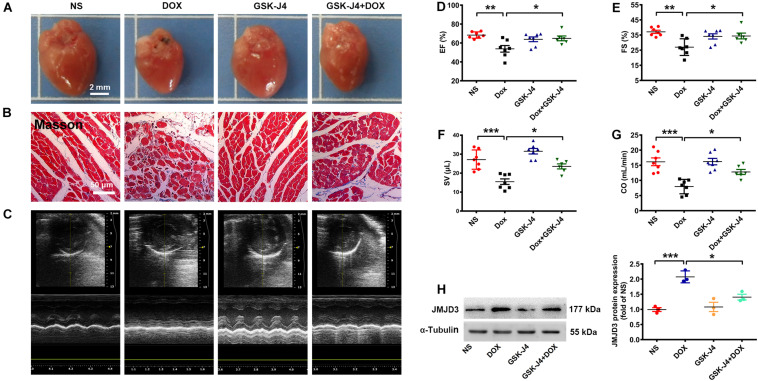
FIGURE 4.
GSK-J4 improved cardiac function of DOX-induced mice cardiotoxicity model. C57BL/6J mice were treated with GSK-J4 (10 mg/kg/day, i.p.) or equal volume of normal saline (NS) for 7 days. After that, the mice were injected with DOX at accumulative dose 28 mg/kg or equal volume of normal saline for 3 weeks. (A) The morphologic changes of gross hearts, scale bar = 2 mm. (B) Pathological changes of hearts tissues were detected by Masson-staining, scale bar = 50 μm. (C) Representative echocardiographic graphs. (D–G) The EF (%), FS (%), SV (μL) and CO (mL/min) were measured by echocardiographic analysis, n = 7. (H) The protein changes of JMJD3 in mice hearts were measured by Western blot. Data were presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. NS group or Dox group. n = 7. CO, cardiac output; DOX, doxorubicin; EF, ejection fraction; FS, fractional shortening; i.p., intraperitoneally injection; JMJD3, Jumonji domain-containing 3; NS, normal saline; SV, Stroke Volume.