Figure 4. The Aedes CO2 receptor is inhibited by isobutyric acid only when Gr1 is present.
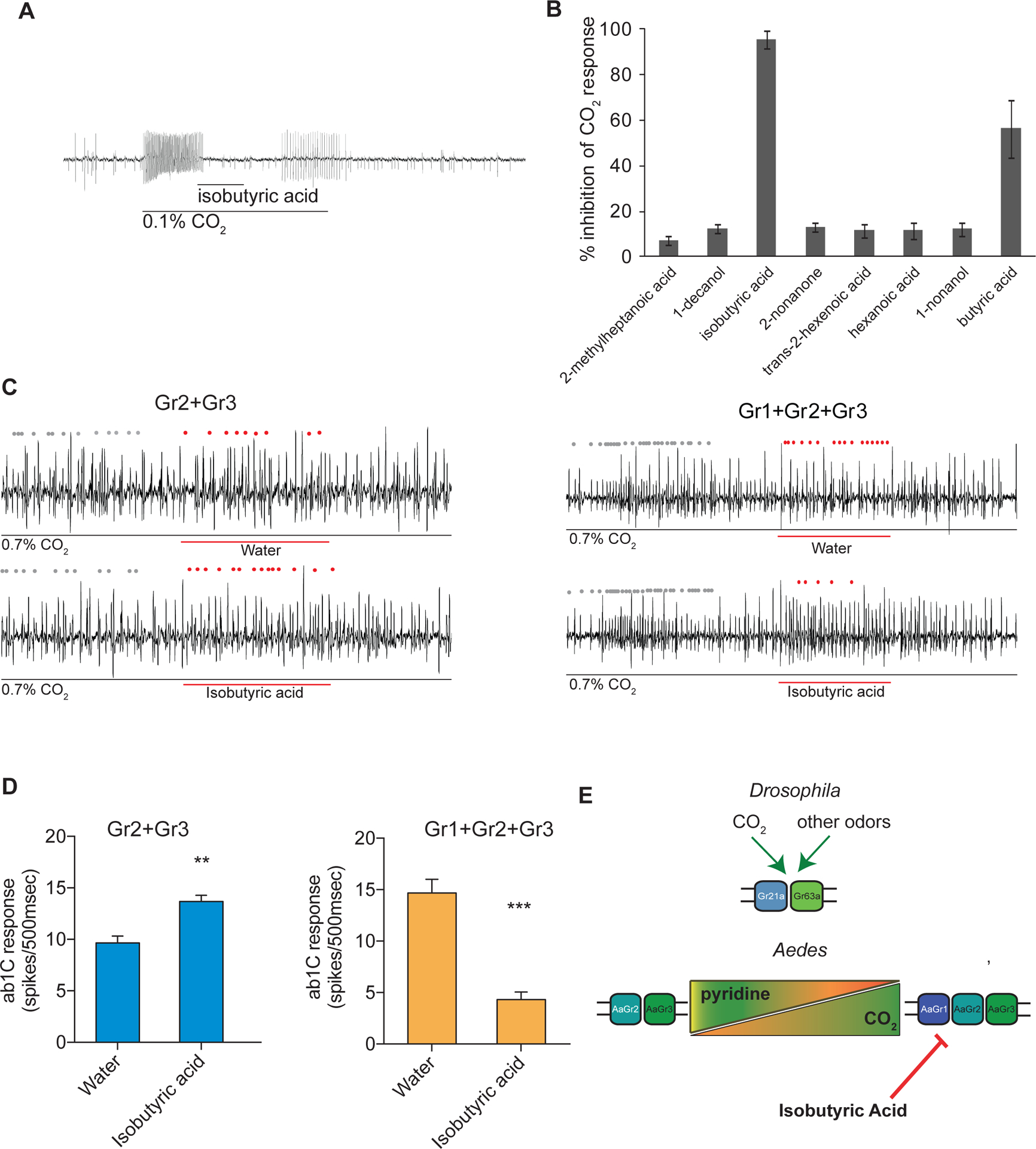
(A) Representative traces of a cpA neuron in female Aedes aegypti responding to CO2 overlaid with isobutyric acid, and (B) mean percent inhibition of cpA responses by odorants relative to solvent. Odorants were diluted at 10% (v/v) in paraffin oil and presented as a 0.5 s stimulus during a 2 s pulse of 0.1% CO2 (n = 5–6). Error bars are s.e.m. (C) Representative traces of a CO2 empty neuron expressing mosquito Grs in D. melanogaster responding to a 2 s pulse of CO2 overlaid with 0.5 s of isobutyric acid or solvent. Dots mark action potentials attributed to the ab1C neuron during part of the baseline and the 0.5 s stimulus window. (D) Mean response of the transgenic ab1C neuron to inhibitor overlay in flies expressing combinations of mosquito Grs (n = 6–9; t-test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). Odorants were diluted at 1% (v/v) in water and presented as a 0.5 s stimulus during a 2 s pulse of 0.7% CO2. Error bars are s.e.m. (E) Model of receptor subunit contributions to odorant response.
