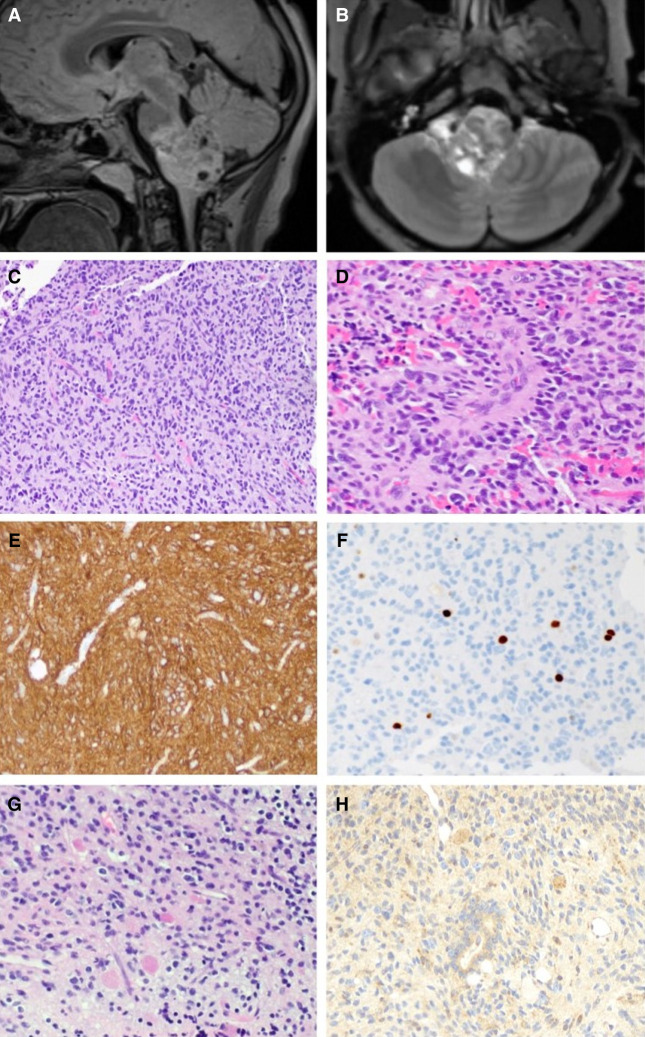
Figure 1.
Radiographic and histologic features of the tumor. Preoperative sagittal T2 FLAIR (A) and axial postcontrast (B) views of preoperative MRI showing a heterogeneous mass centered in the medulla and projecting into the fourth ventricle. (C) A representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained section reveals a diffusely infiltrating glial neoplasm with round-to-oval nuclei and variable perinuclear clearing amid thin-walled capillaries. (D) Some neoplastic cells are arranged around blood vessels. Several tumor cells have vesicular nuclei and mild-moderate pleomorphism. (E) The neoplastic cells are strongly and diffusely positive for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). (F) The Ki-67 antibody labels a subset of cells, with 2.4% of cells staining positive in this field. (G) Abundant eosinophilic granular bodies are scattered throughout the neoplasm. (H) A VPS35 monoclonal antibody strongly highlights the eosinophilic granular bodies, and variable immunoreactivity is seen in the tumor cells. Magnifications, 20× (C,E–H) and 40× (D).