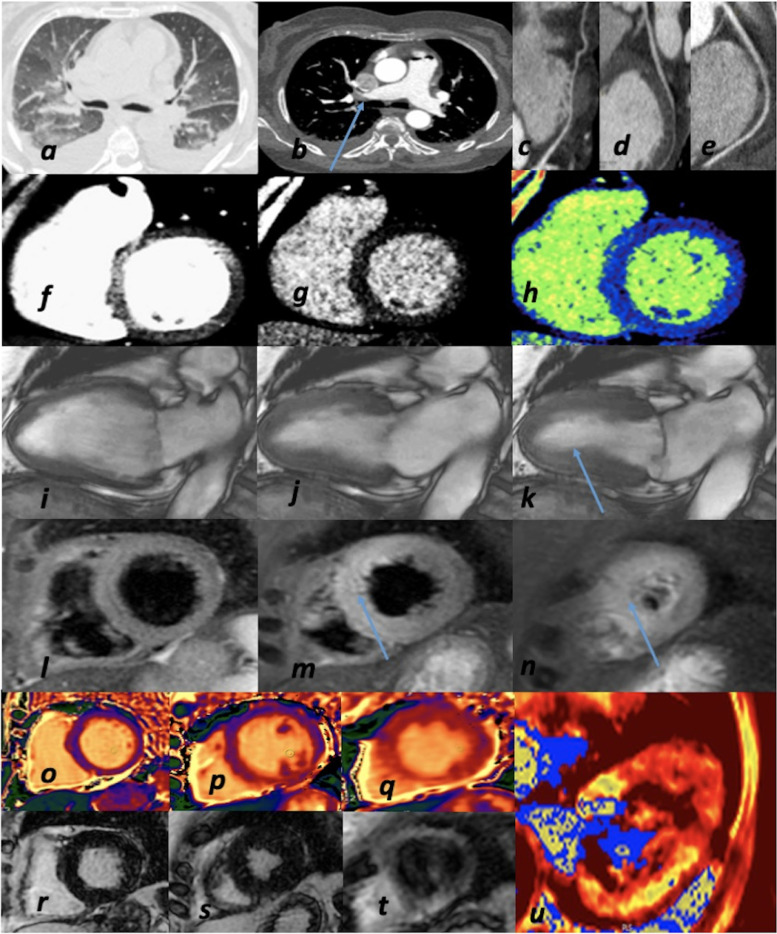
Fig. 5.
Comprehensive and advanced imaging in a COVID-19 patient. Severe acute respiratory distress in 66-year-old woman. (a) Chest CT: bilateral pleural effusion and common pattern of pulmonary edema and interstitial pneumonia; (b) CTPA: bilateral PE (arrow); (c-d-e) CCTA: coronary arteries: absence of obstructive CAD (LAD-c; LCx-d; RCA-e); f) CT: contrast-enhanced first pass myocardial perfusion imaging-left ventricle SAx view; (g) CT-late scan with color-map (h): after seven minutes absence of myocardial delayed enhancement); (i-j-k) CMR-functional CINE sequences: mild hypokinesis of LV apex (arrow) with improved LV EF (47%) as compared to TTE at 1st day; (l-m-n) CMR-TIR T2 sequences: hyperintense signal> mid-apical edema (arrow); (o-p-q) CMR-native T1 mapping: normal T1 mapping values; (r-s-t) CMR-post- contrast sequences: no LGE (late gadolinium enhancement); (u) CMR-T2 mapping: increased T2 values of LV apex (myocardial edema). Diagnosis: pulmonary edema due to TTS in concomitant PE.CAD, coronary artery disease; CCTA, coronary computed tomography angiography; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; CT, computed tomography; CTPA, computed tomography pulmonary angiography; EF, ejection fraction; LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; LCx, left circumflex coronary artery; LV, left ventricular; LGE, late gadolinium enhancement; MI, myocardial infarction; PE, pulmonary embolism; RCA, right coronary artery; SAx, short axis; TIR T2, triple inversion recovery T2-weighted; TTE, transthoracic echocardiography; TTS, takotsubo syndrome.