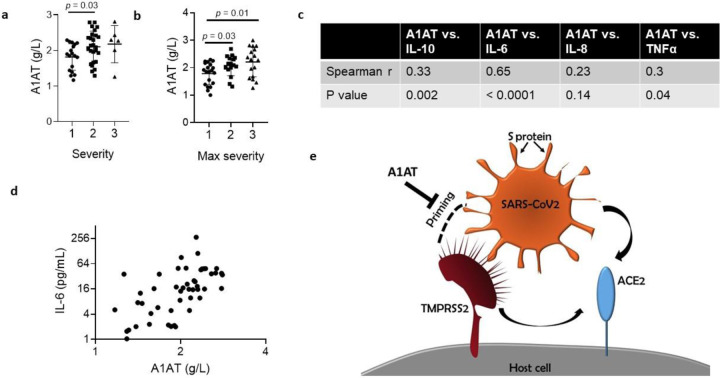
Figure 5. A1AT concentration in plasma samples of patients with COVID-19 and suggested role in SARS-CoV-2 cell entry.
A1AT plasma concentrations in patients who were positive for COVID-19 are shown and stratified according to disease severity at the time of disposition from the Emergency Department (a) or the maximal severity within 30 days of index Emergency Department visit (Max severity) (b) (1 = Outpatient, 2 = Hospitalized, 3 = Intensive Care Unit or Death). In (c), correlation between plasma A1AT concentrations and plasma IL-10, IL-6, IL-8, or TNFα concentrations. r and p values were calculated according to Spearman correlation. d. plasma concentration of A1AT and IL-6 in each patient with confirmed COVID-19 with markers representing individual patients. A1AT, alpha 1 antitrypsin; IL, interleukin. e. Model of SARS-CoV-2 entry mediated by extracellular proteolytic events. Extracellular proteases, such as TMPRSS2, process the S protein on the SARS-CoV-2 envelope in a process called priming. Priming of the S protein is necessary for binding between the S protein and the host receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Extracellular inhibitors, such as alpha 1 antitrypsin (A1AT), prevent the priming of the S protein and inhibit virus entry. In addition, inhibiting transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) prevents processing of ACE2, which decreases the infectivity of the coronavirus.