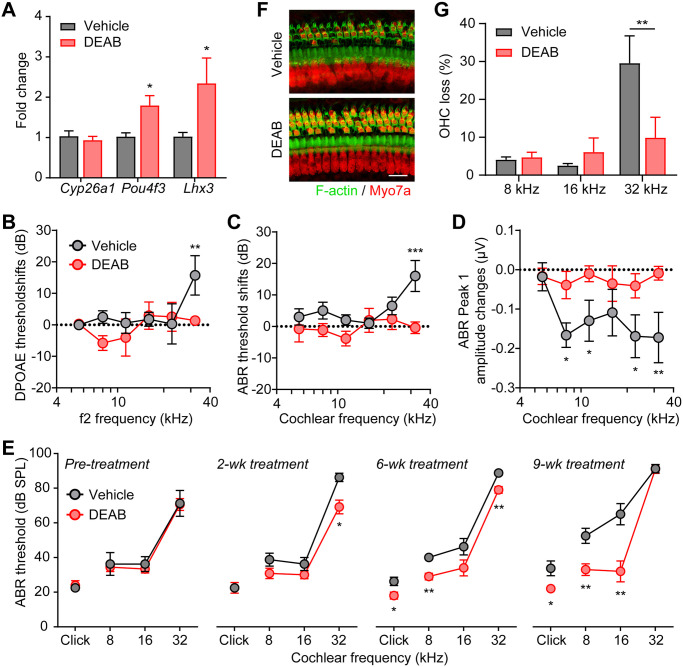
Fig 5. Inhibition of RA signaling rescues auditory function in Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice.
(A) Upregulation of Pou4f3 and Lhx3 mRNA expression in Pou4f3(Δ/+) cochleae by DEAB treatment in vivo. DEAB or DMSO vehicle were injected intraperitoneally daily to 3 months old Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice for 4 weeks. * P < 0.05 by unpaired student’s t-test, n = 4–6 mice. (B) DPOAE threshold shifts, (C) ABR threshold shifts and (D) ABR P1 amplitude changes in 3 months old Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice treated intraperitoneally daily with either vehicle control or DEAB for 3 weeks. The threshold shifts or amplitude changes were calculated by differences between pre- and 3 weeks post treatment. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA, n = 10–13 mice of each treatment. (E) ABR thresholds of Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice treated intraperitoneally daily with either vehicle or DEAB for 2, 6 and 9 weeks. Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice were 2 months old prior to treatment. * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.01 by unpaired student’s t-test, n = 4–6 mice for each treatment. (F) Myo7a immunostaining images of the cochlear sensory epithelia (32 kHz region) from Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice treated with vehicle or DEAB for 9 weeks. Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice were 2 months old prior to treatment. Hair cells and F-actin was labelled with Myo7a (red) and Alexa Fluor 488-Phalloidin (green), respectively. Scale bar was 20 μm. (G) Percentage of outer hair cell loss of Pou4f3(Δ/+) mice treated with vehicle or DEAB for 9 weeks. ** P < 0.01 by unpaired student’s t-test, n = 5–10 cochleae for each treatment.