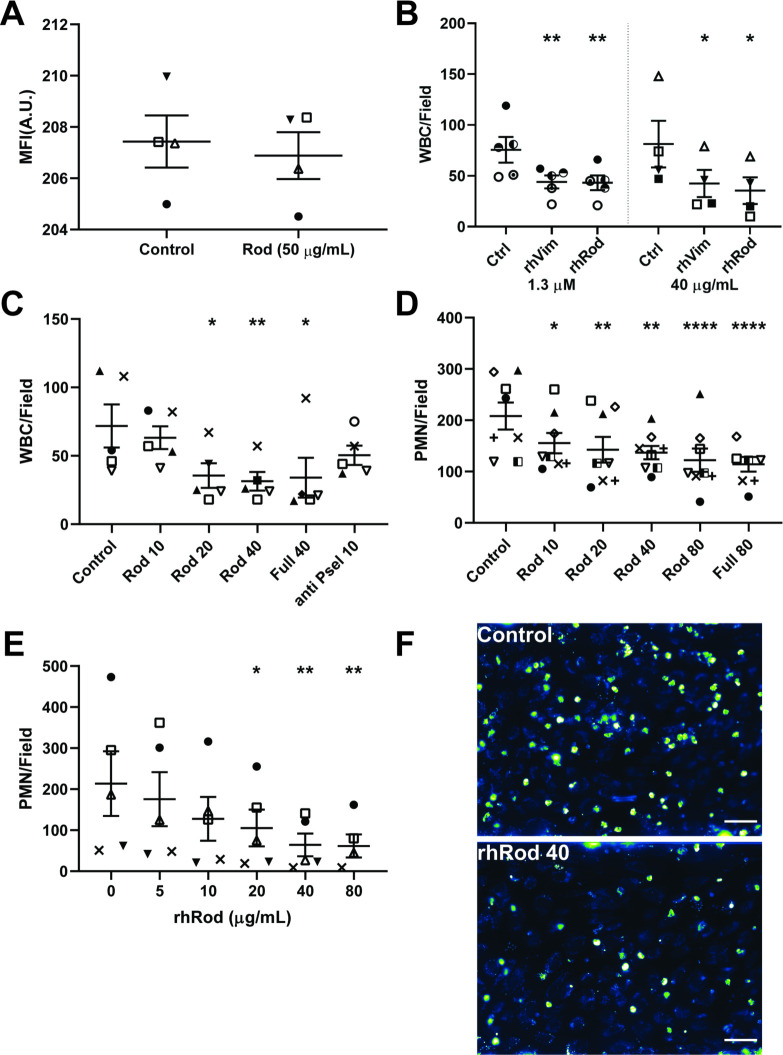
Fig 5. rhRod blocks leukocyte adhesion to platelets, inflamed endothelium, and P-selectin-coated channels.
(A) Mepacrine-labeled whole blood perfusing over fibrin(ogen)-coated channels at 5 dyn/cm2. rhRod did not affect platelet adhesion to fibrin(ogen)-coated channels, based on mean fluorescence intensity. (B) rhRod decreased leukocyte adhesion to fibrin(ogen)-captured platelets similar to rhVim at equal molar (1.3 μM) and mass (40 μg/mL) concentrations. (C) rhRod decreased leukocyte adhesion to IL1β/IL4-co-stimulated HUVEC. (D) rhRod also decreased isolated PMN adhesion to IL1β/IL4-co-stimulated HUVEC. (E) Finally, rhRod decreased isolated PMN adhesion to P-selectin coated channels in a dose dependent fashion. Leukoocyte adhesion was measured at shear stress of 2 dyn/cm2. (F) Representative images of mepacrine-labeled whole blood leukocytes perfused over IL1β/IL4 co-stimulated HUVEC in the presence of control buffer (top) and rhRod 40 μg/mL (bottom). Each subject is represented by a unique symbol. Scale bar = 50 μm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, & ****p<0.001.