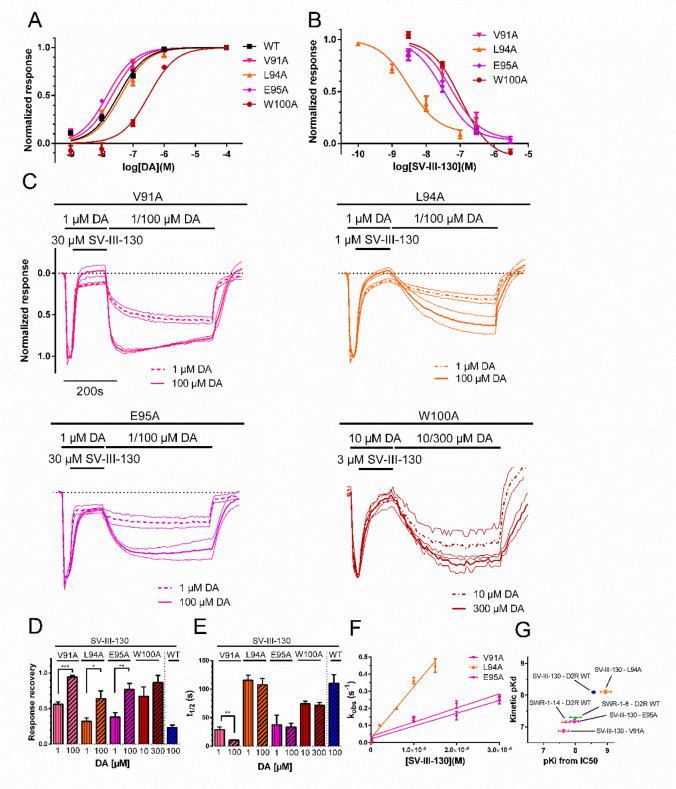
Figure 3.
Potencies, recovery from antagonism, and binding kinetics of SV-III-130 at the V91A, L94A, and E95A mutant D2R. A) DA potency at V91A (EC50 = 21 nM, n = 3–4), L94A (EC50 = 41 nM, n = 3–7), E95A (EC50 = 15 nM, n = 3–4), W100A (EC50 = 323 nM, n = 3), and WT (EC50 = 33 nM, n = 4) D2R. B) SV-III-130 potency at the V91A (n = 4), L94A (n = 3), E95A (n = 7), and W100A (n = 3) D2R. C) Recovery of activation by DA at the V91A (n = 3 for 1 μM DA and n = 4 for 100 μM DA), L94A (n = 13 for 1 μM DA and n = 13 for 100 μM DA), E95A (n = 5 for 1 μM DA and n = 3 for 100 μM DA), and W100A (n = 4 for 10 μM DA and n = 4 for 300 μM DA) mutant D2R following antagonism by SV-III-130. GIRK current traces normalized to the maximal response evoked by 1 μM (10 μM for W100A) DA. Thick lines represent mean normalized currents, whereas thin lines indicate SEM. D) Extent of recovery upon application of 1 or 100 μM (10 and 300 μM for W100A) DA following antagonism by 30 μM (V91A and E95A), 3 μM (W100A), and 1 μM SV-III-130 (L94A; data from experiments shown in panel C). E) Rate of recovery following application of 1 or 100 μM DA (10 and 300 μM for W100A; data from experiments shown in panel C). F) Observed association rates, kobs, which allowed for calculation of association rates for SV-III-130 at the V91A, L94A, and E95A D2R. n = 3–7. G) Clustering of kinetic Kd relative to Ki for SWR-1-8, SWR-1-14, and SV-III-130 at the WT receptor and SV-III-130 at the V91A, L94A, and E95A mutant receptors, as indicated. Data shown are means ± SEM *; p < 0.05, **; p < 0.01, and ***; p < 0.001, Student’s t test.