Figure 5.
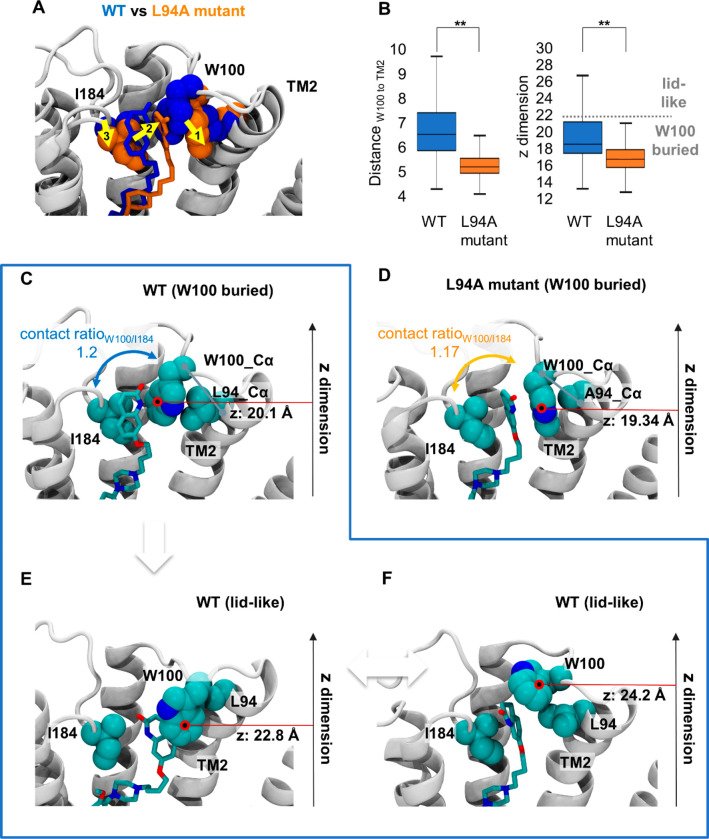
Structural impact of L94A mutation on SV-III-130. A) The most populated SV-III-130 binding mode in the D2R WT (blue) and the L94A (orange) receptors. Upon L94A mutation, the ligand translates toward transmembrane segment 2 as indicated by the yellow arrows. Despite translation in the L94A mutant, SV-III-130 is primarily sandwiched by W100 and I184 similar to the WT complex. B) Comparison of the position of W100 between the WT and L94A receptors in terms of distance between Cα atoms of W100 and L/A94, as well as the position of the W100 side chain center of mass in the z-dimension (perpendicular to the membrane). Both values are significantly different between the WT and the L94A receptors. C) Representative ligand binding mode in the WT receptor with W100 adopting a low z value (putative RL complex). D) Representative ligand binding mode in the L94A mutant receptor with W100 adopting a low z value (putative RL complex). E, F) Ligand binding modes in the WT receptor in which W100 adopts higher z values and stacks on top of the ligand (potentially leading to RL* complexes). In C–F), the position of the center of mass of the W100 side chain (red circle) in the z-dimension (perpendicular to the membrane) is highlighted. **; p < 0.01, Mann–Whitney U test.