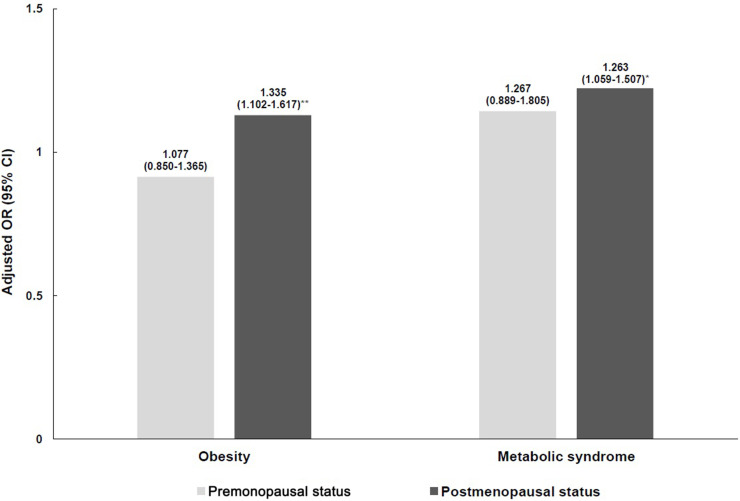
Figure 1.
Adjusted odds ratio for obesity and metabolic syndrome according to menopausal status and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration. Obesity was defined as BMI ≥25.0 kg/m2 by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Metabolic syndrome was defined if ≥ 3 following diagnostic criteria by the modified National Cholesterol Education Program/Adult Treatment Panel III: 1) WC ≥85 cm according to the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, 2) TGs ≥150 mg/dL or receiving treatment for high TGs, 3) HDL-C <50 mg/dL or receiving treatment for low HDL-C, 4) BP ≥130/85 mmHg or receiving treatment for high BP, and 5) FG ≥100 mg/dL or receiving treatment for hyperglycemia. The odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) were calculated in reference to a serum vitamin D concentration ≥50 nmol/L using multivariate logistic regression adjusting for age, education level, household income, marital status, residential region, subjective stress level, dietary supplement consumption, smoking status, alcohol consumption status, and regular exercise (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01).