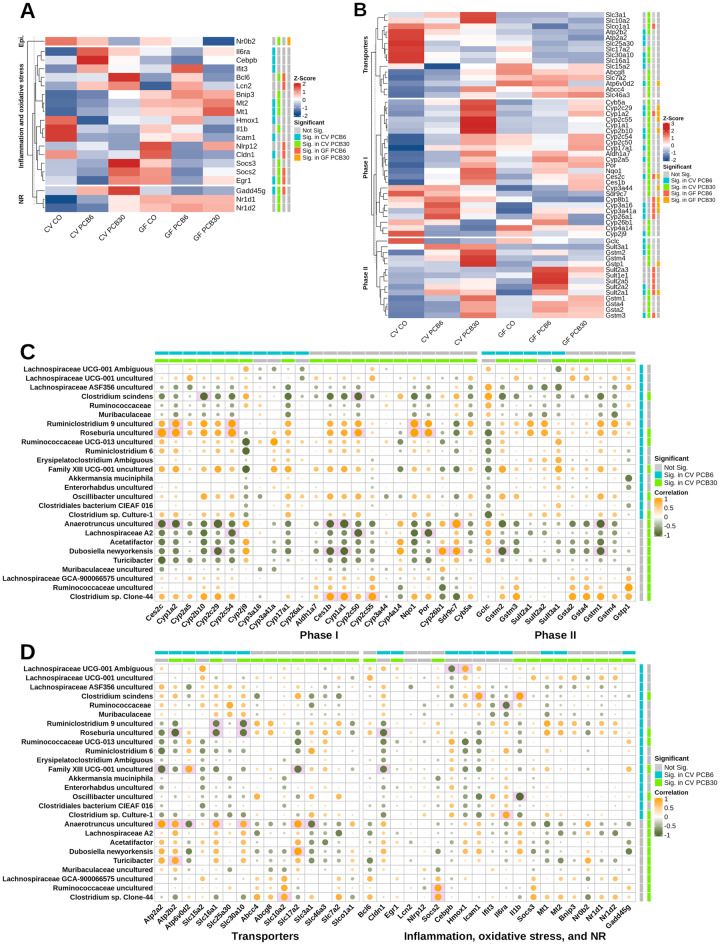
Figure 5.
Relative expression of differentially regulated genes grouped by functional categories and correlation of differentially abundant bacteria and differentially regulated genes in conventional mice. A, Scaled expression of genes in epigenetic modification (Epi.), inflammation and oxidative stress, and nuclear receptor (NR) categories for conventional and germ-free (GF) mice. Differential regulation (Significant) information is provided on the colored bar (ie, blue shows differential expression for conventional mice exposed to polychlorinated biphenyl [PCB] 6 mg/kg and gray indicates genes that are not differentially regulated). B, Scaled expression of genes in phase-I, -II, and transporter categories for conventional and GF mice. Differential regulation (Significant) information is provided on the colored bar (ie, blue shows differential expression for conventional mice exposed to PCB 6 mg/kg and gray indicates genes that are not differentially regulated). Spearman correlation for differentially abundant bacteria (rows) and differentially regulated genes (columns) in phase-I and -II (C), and transporters, inflammation and oxidative stress, and NR categories (D). Green-orange color scale represents the direction of correlation and sizes of circles show strength of association. Differential abundant bacteria and metabolites are shown as blue and green colored bars, representing significance for mice exposed to PCB 6 and 30 mg/kg, respectively. Pink filled box indicates significant correlation at FDR < 0.1 with absolute spearman’s ρ > .8. Abbreviation: CV, conventional.