Figure 1.
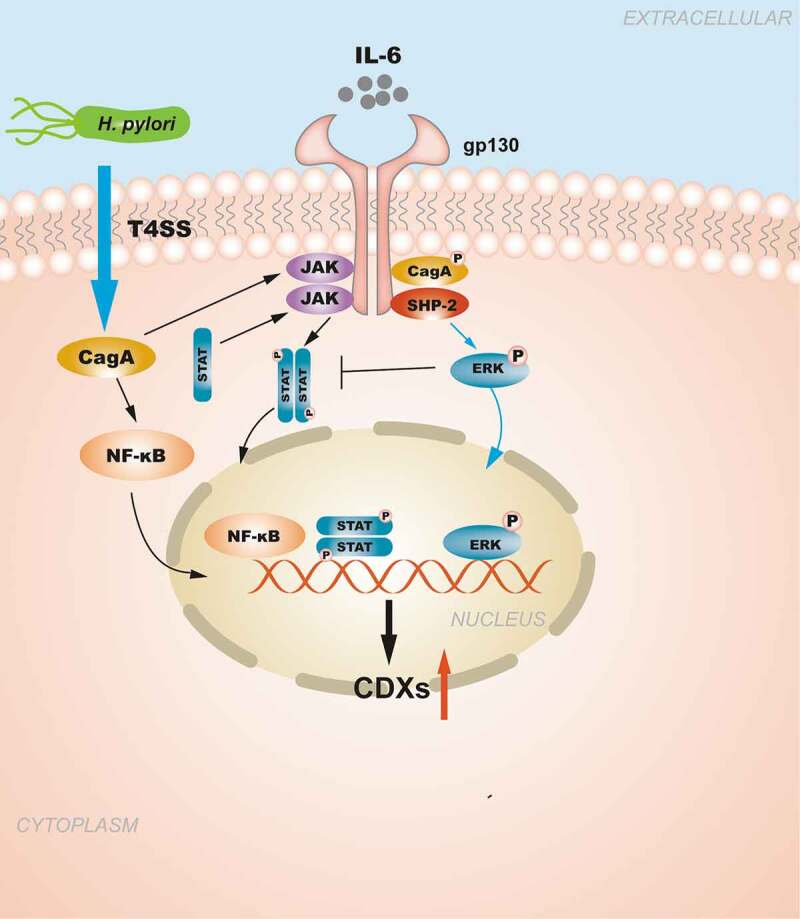
The regulation of CDXs in GIM induced by NF-κB signaling pathway and pro-inflammatory cytokines. H. pylori injects the oncoprotein CagA into gastric epithelial cells using a type IV secretion system (T4SS) to activate the NF-κB signaling pathway. NF-κB activation induces the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6, and IL-6 binds to its specific receptor gp130, activating two major signaling pathways: SHP-2/ERK and JAK/STAT. CagA can also affect the signal transduction of gp130 regulation, and the resulting biological effect depends on the tyrosine phosphorylation status of CagA. Moreover, the SHP2/ERK and JAK/STAT signaling pathways are considered to play opposite roles in gastric epithelial cells.
