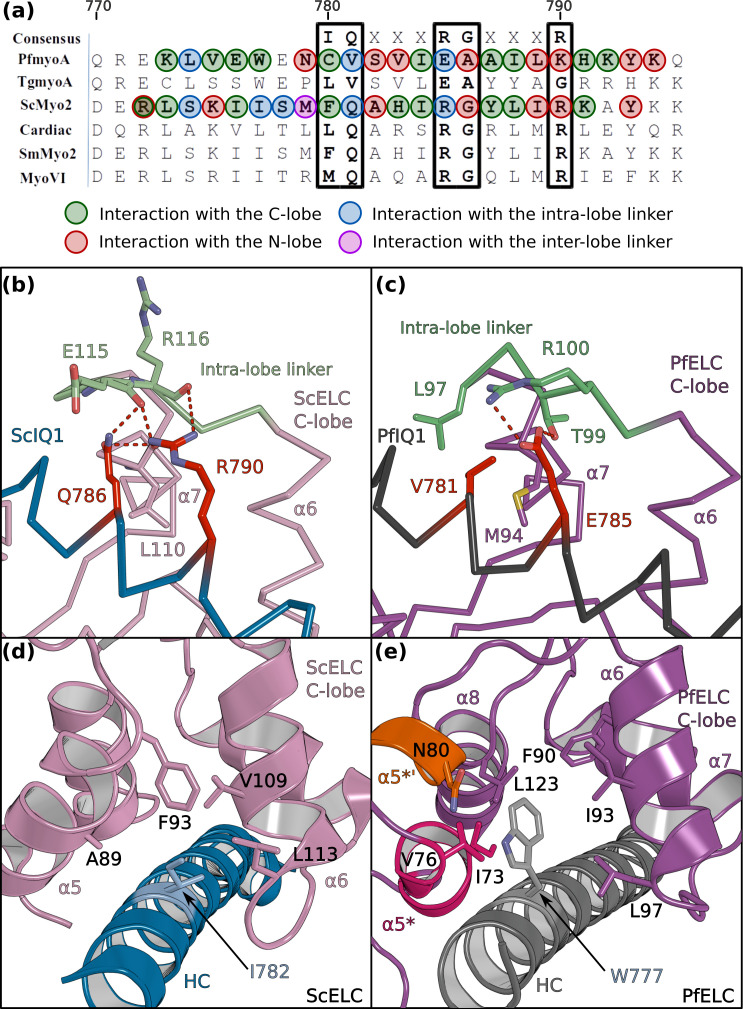
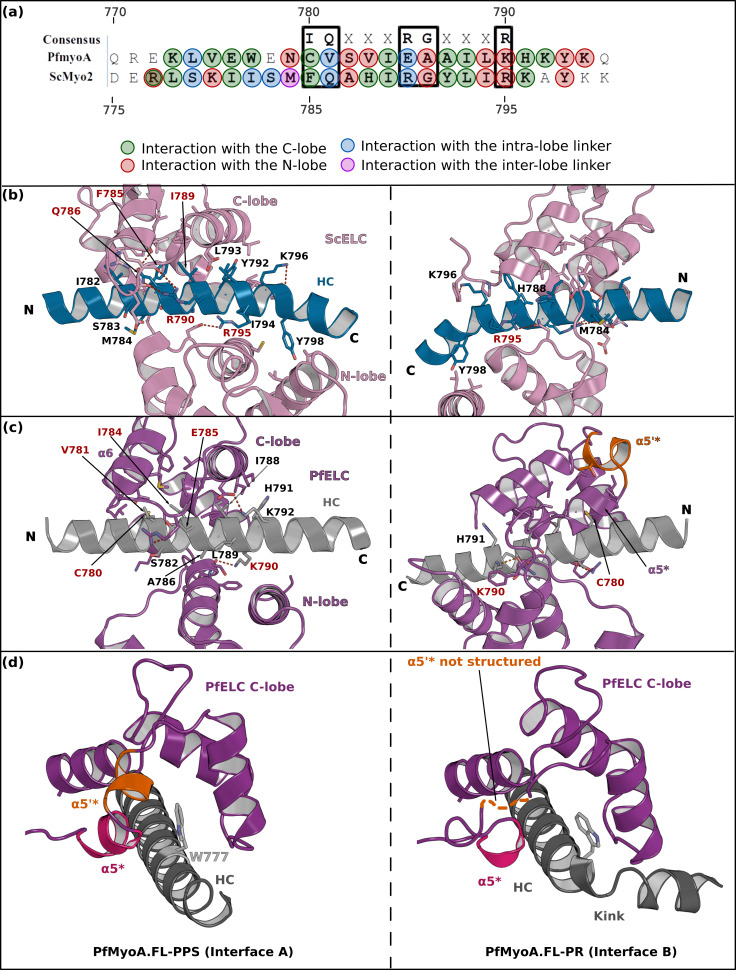
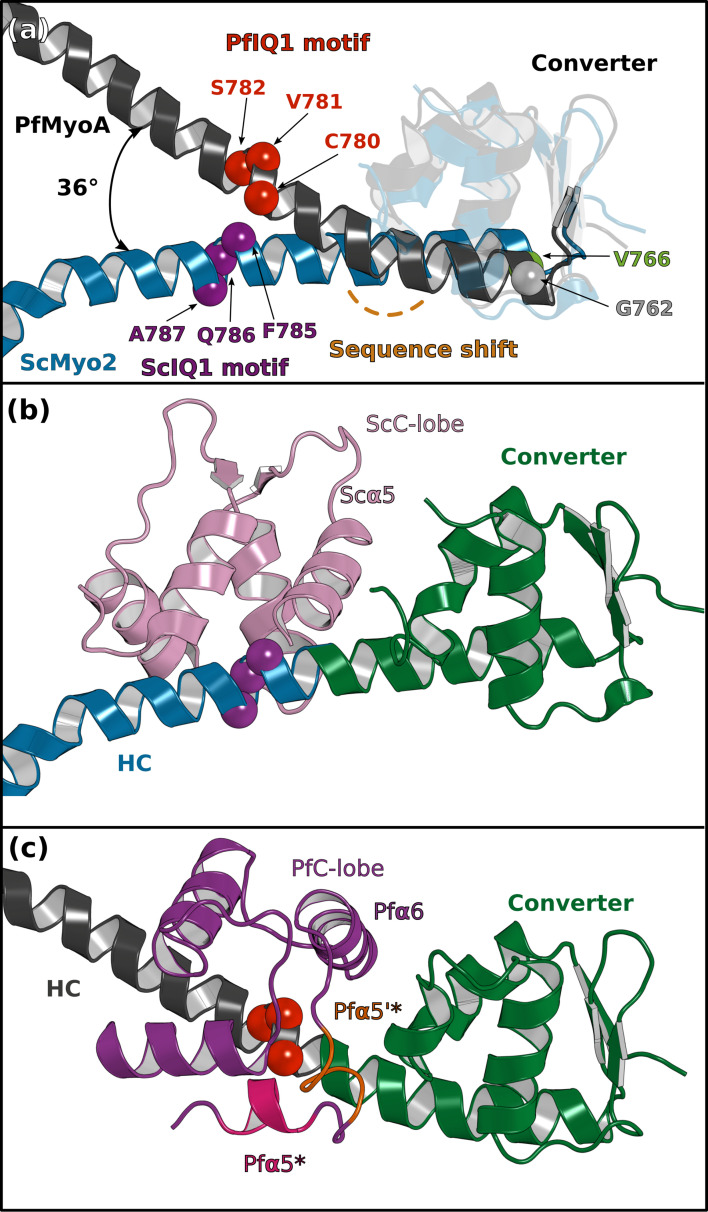
Figure 4. PfELC binds a degenerate IQ motif.
(a) Sequence alignment of PfMyoA IQ1 to the consensus IQ motif and IQ motifs from other myosins: MyoA from Toxoplasma gondii (TgmyoA); bay scallop (Argopecten irradians) myosin 2 (ScMyo2); human (Homo sapiens) β-cardiac myosin 2 (Cardiac); human smooth muscle myosin 2 (SmMyo2); human myosin 6 (MyoVI). Consensus residues are contoured by a black box. (b) The intra-lobe linker of the scallop C-lobe interacts with the HC consensus residues with polar contacts. (c) In contrast, the intra-lobe linker of the Pf C-lobe is predominantly bound to the HC with apolar contacts. (d,e) Intra-lobe interactions maintain the semi-open C-lobe. Specificity in the recognition of the PfELC occurs via the W777 residue in PfMyoA. (d) In conventional myosins such as ScMyo2, a small side chain (I782) is found at the equivalent position, contributing to few interactions within the semi-open lobe. (e) In PfMyoA the bulky Trp (W777) is sandwiched between the α5*, α5’* and α6 helices, increasing the hydrophobic interactions with the PfELC C-lobe.