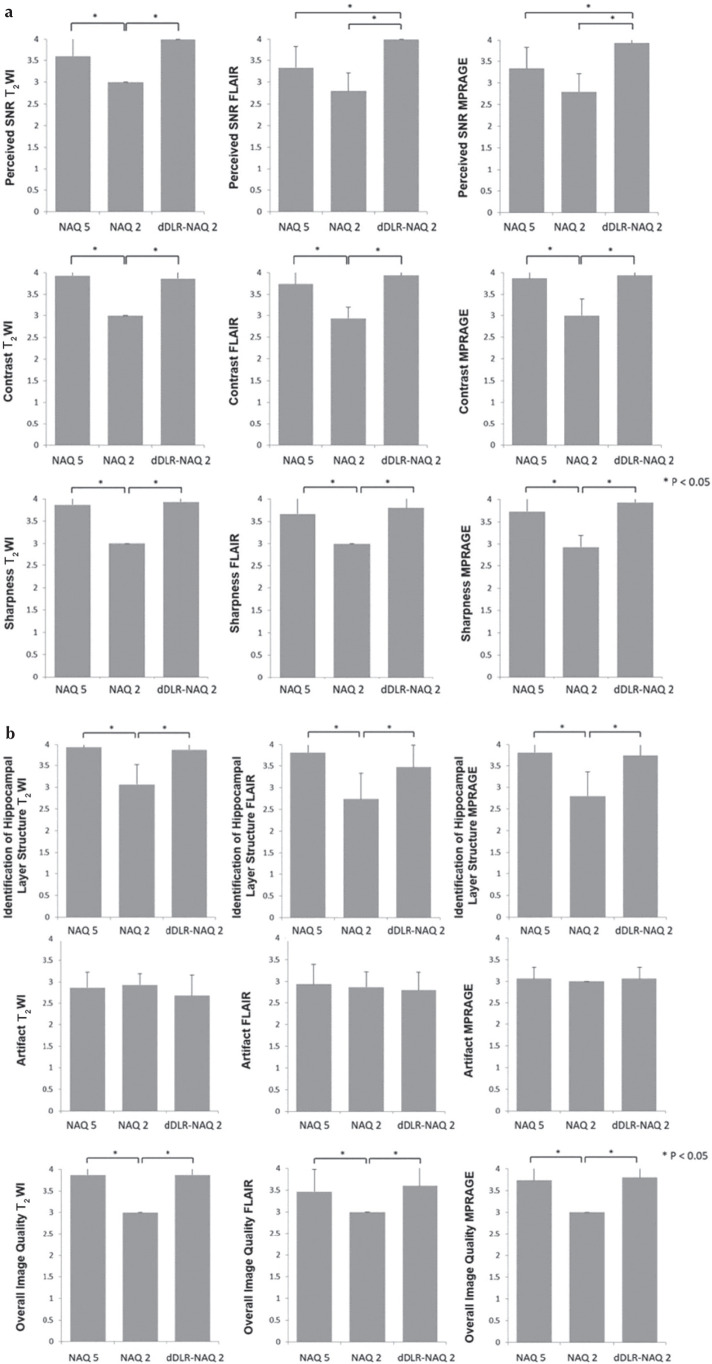
Fig. 6.
(a) Results of qualitative assessments: perceived SNR, image contrast and image sharpness. Perceived SNR of dDLR-NAQ2 was significantly higher than that of NAQ2 in all sequences (P < 0.05). Perceived SNR of NAQ5 was significantly higher than that of NAQ2 in T2WI (P < 0.05). In FLAIR and MPRAGE, perceived SNR of dDLR-NAQ2 was significantly higher than that of NAQ5 (both P < 0.05). Image contrast for both dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 was significantly higher than that of NAQ2 in all sequences (P < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 (T2WI: P = 0.95; FLAIR: P = 0.64; MPRAGE: P = 0.95). For image sharpness, dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 were both significantly superior to NAQ2 in all sequences (P < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 (T2WI: P = 0.95; FLAIR: P = 0.79; MPRAGE: P = 0.64). (b) Results of qualitative assessments: identification of hippocampal layer structure, artifact and overall image quality. For identification of hippocampal layer structure, dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 were both significantly superior to NAQ2 in all sequences (P < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 (T2WI: P = 0.94; FLAIR: P = 0.38; MPRAGE: P = 0.91). There were no significant differences in artifacts between NAQ5, NAQ2 and dDLR-NAQ2 (T2WI: P = 0.20; FLAIR: P = 0.47; MPRAGE: P = 0.37). For overall image quality, dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 were both significantly superior to NAQ2 for all sequences (P < 0.05), and there was no significant difference between dDLR-NAQ2 and NAQ5 (T2WI: P = 1.00; FLAIR: P = 0.72; MPRAGE: P = 0.94). FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; dDLR, deep learning-based reconstruction; NAQ, number of image acquisition; MPRAGE, magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo; T2WI, T2-weighted image.