Fig. 7.
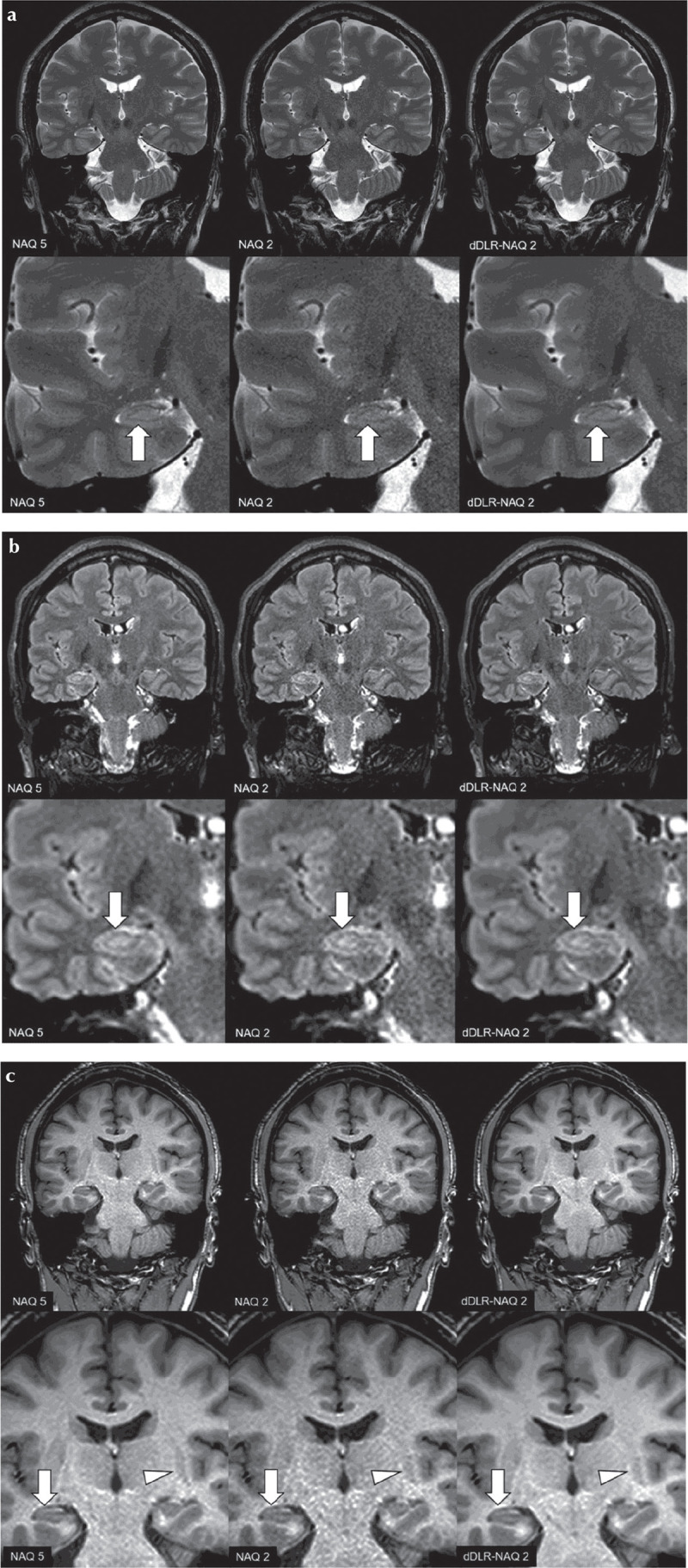
A 38-year-old male healthy volunteer. Upper row: original magnification, lower row: magnified image. (a) T2-weighted image (T2WI): A NAQ2 has higher image noise than NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2. Identification of the hippocampal layer structure is superior in both NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2 compared with NAQ2 (arrows). (b) FLAIR: NAQ2 demonstrates higher image noise than NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2. Identification of the hippocampal layer structure is again superior in NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2 compared with NAQ2 (arrows). (c) magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo (MPRAGE) NAQ2 demonstrates higher image noise than NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2. Identification of the hippocampal layer structure is superior in NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2 compared with NAQ2 (arrows). Contrast between the left putamen and its surrounding white matter is also superior in NAQ5 and dDLR-NAQ2 compared with NAQ2 (arrowheads). dDLR, deep learning-based reconstruction; NAQ, number of image acquisition.
