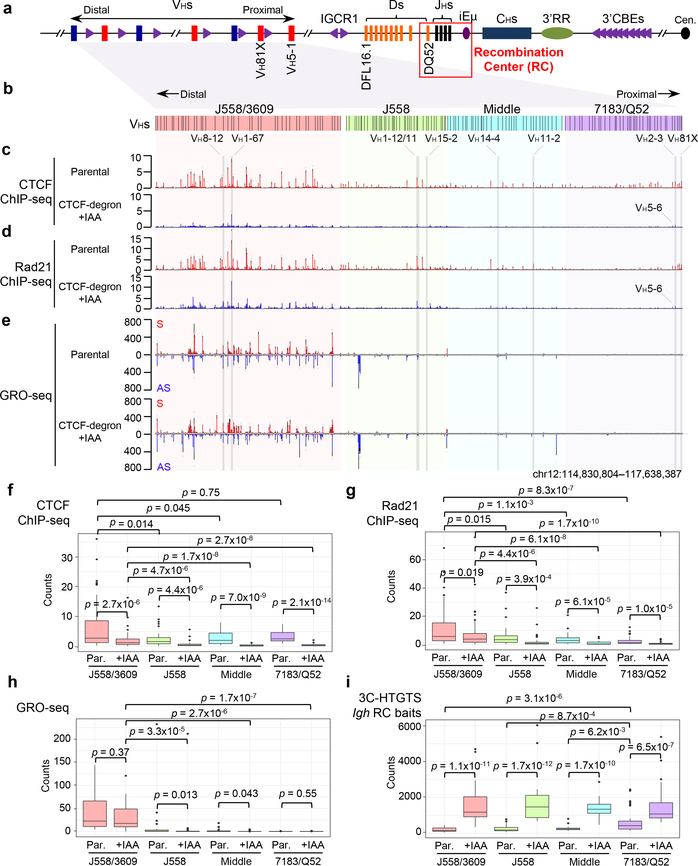
Fig. 2 |. Characterization of chromatin CTCF/Rad21-binding and transcription across the VH locus in G1-arrested parental and IAA-treated CTCF-degron cells.
a, Schematic of the entire murine Igh locus with details as shown in Fig. 1a. b, The four VH domains are highlighted different colors which are maintained in related figures. c-e, Average signal counts ± s.e.m. of CTCF (c) and Rad21 (d) ChIP-seq and GRO-seq (e) from three biologically independent experiments across the four highlighted VH domains in G1-arrested parental and IAA-treated CTCF-degron cells are plotted. S/AS: sense/anti-sense transcription. See Extended Data Fig. 4a,b and 5a for the plots across other parts of Igh locus. VHs for comparisons in Fig. 3 are highlighted. f-i, Box-and-Whisker plots are presented with median, upper and lower quartiles and whiskers showing 1.5x interquartile range for CTCF (f) and Rad21 (g) ChIP-seq, GRO-seq (h), and 3C-HTGTS (i) signal counts within indicated VH domains in G1-arrested parental (“Par.”) and IAA-treated CTCF-degron cells. n=3 biological repeats with similar results for each condition in f-i. p values were calculated using two-sided Mann-Whitney U test. See Methods for details. Comparison of panels (f) and (h) reveals that residual CTCF binding levels are significantly higher in the highly transcribed distal VH domain than those of the proximal domains with less overall transcription, which might reflect known roles of transcription in CTCF chromatin binding33,34.