Figure 2. ALK1-OE rescues the vascular phenotypes of ENG- as well as ALK1-deficient mice.
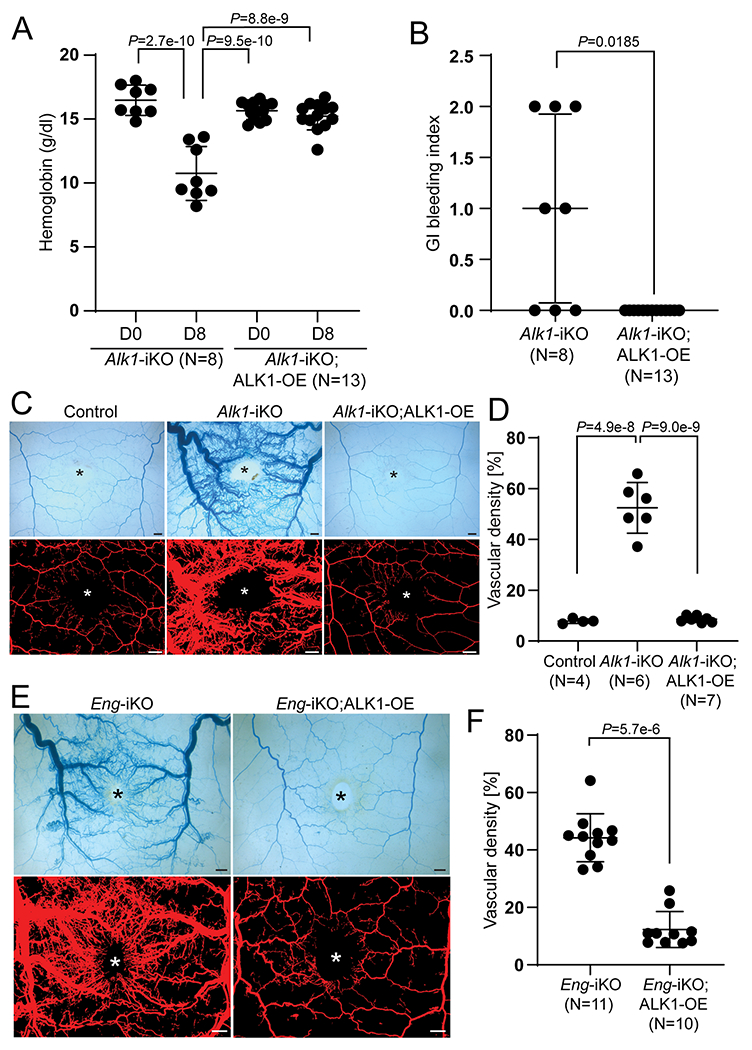
A, Alteration of hemoglobin levels in SclCreER;Alk1-iKO (n=8) and SclCreER;Alk1-iKO;ALK1-OE (n=13) on the first day (D0) and 8 days (D8). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. B, Gastrointestinal hemorrhage index of SclCreER;Alk1-iKO (n=8) and SclCreER;Alk1-iKO;ALK1-OE (n=13) mice. The unpaired t-test was performed for statistical analysis. Welch t-test. C, Representative images of latex dye-perfused blood vessels (upper panels) and processed images (lower panels) on the dorsal skin of control (SclCreER-negative Alk1-iKO;ALK1-OE (n=4), SclCreER;Alk1-iKO (n=6), and SclCreER;Alk1-iKO;ALK1-OE (n=7) mice on 8 days after wounding. D, Quantification of the vascular area containing latex with the processed images. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. E, Latex perfusion images in SclCreER;Eng-iKO (n=11) and SclCreER;Eng-iKO;ALK1-OE (n=10). F, Quantification of vascular density containing latex. Mann-Whitney test. All data are means ± SDs. The wound sites are marked by asterisks. Scale bars: 1 mm.
