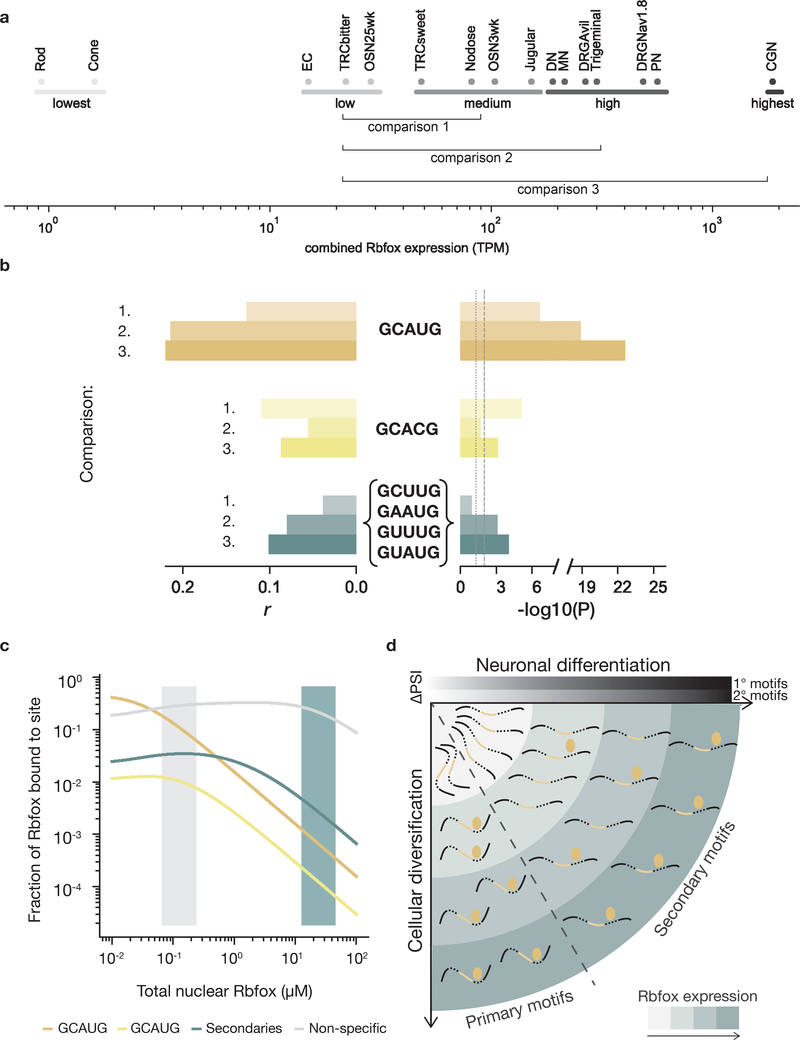
Figure 6. Secondary motifs are active in neuronal cell types with high Rbfox expression.
a. Differentiated neuronal cell types from Weyn-Vanhentenryck et al.4 (SRA SRP055008), arranged by combined Rbfox1, Rbfox2, and Rbfox3 expression (log10 of sum of RPKM values). Cell types were grouped into Lowest, Low, Medium, High, and Highest Rbfox expression categories. Cells analyzed: olfactory sensory neurons (OMP+) (OSN), enterochromaffin cells (EC), taste receptor cells (TRC), rod or cone photoreceptors, jugular or nodose visceral sensory ganglia, dopaminergic neurons (DN), motor neurons (MN), dorsal root ganglia sensory neurons (Nav1.8+ or Avil+) (DRG), trigeminal ganglia, Purkinje neurons (PN), and cerebellar granule neurons (CGN). b. Linear regression of 1,909 alternatively spliced exons comparing the Rbfox expression groups indicated in a. Horizontal bars represent the Pearson r value (left) and uncorrected significance (right) of the correlation between the number of occurrences of primary or secondary (GCUUG, GAAUG, GUUUG, and GUAUG) motifs and ΔPSI values between Medium and Low (1.), between High and Low (2.), or between Highest and Low (3.) Rbfox expression regimes. Grey dotted and dashed lines indicate 0.05 and 0.01 significance thresholds, respectively. c. An equilibrium model for Rbfox binding to intronic sequences in the nucleus at various expression levels of Rbfox (low, grey area; high, teal area). GCAUG indicated by gold, GCACG indicated by yellow, secondary motifs indicated in teal, non-specific 5mers in grey. d. Graphical summary of how Rbfox proteins (golden ellipses) regulate distinct splicing events at different expression levels (teal shading). Secondary motifs are functionally relevant only at higher Rbfox levels, occurring at later stages of neuronal differentiation or in cell types with high Rbfox expression, while primary motifs are functionally relevant at earlier stages and in cell types with medium as well as high Rbfox levels.