Figure 7. Integration of chromatin state and gene expression identifies genes important for human cardiac development.
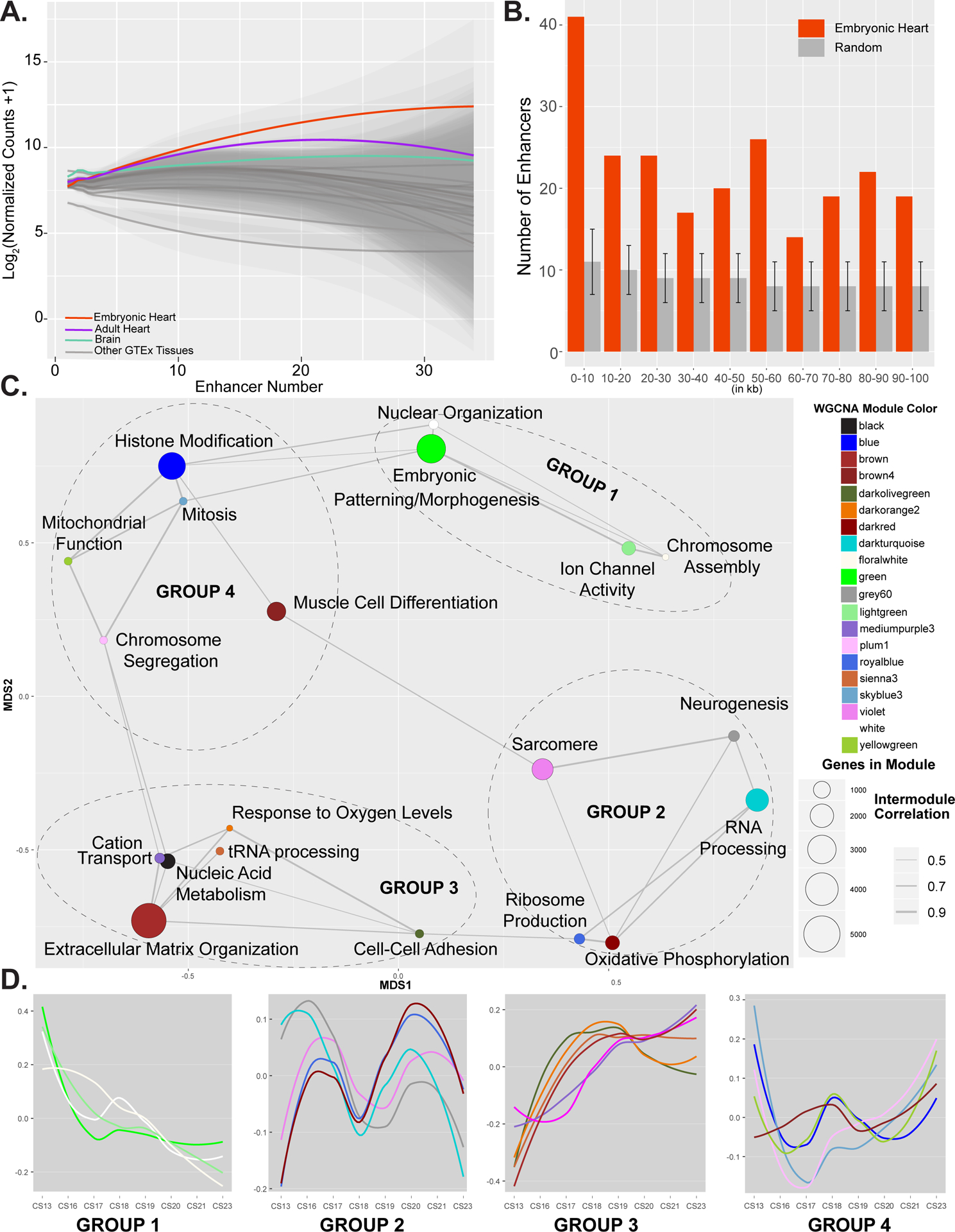
A. Plot of gene expression values from embryonic heart (red), adult heart (purple), brain (green) or all other tissues (grey) for genes assigned indicated number of EHEs as determined by GREAT. Genes assigned multiple EHEs are more strongly expressed in embryonic heart than other tissues. Significant differences in distributions of gene expression values in each comparison were determined based on Mann-Whitney test. B. Histogram of distances of EHEs (red) or randomly selected sets of enhancers (grey) to the nearest heart specific gene (GINI > 0.75) in 10 kb bins up to 100 kb. Overall EHEs are enriched near heart specific genes over all distances up to 100 kb. Error bars indicate standard deviation of 1000 random permutations of enhancers. C. Network plot of gene modules identified by WGCNA using embryonic heart gene expression data. A pearson correlation of the module eigenvectors was calculated for the edges. Positive correlations of 0.5 and greater were included. The location of each module is determined by multiple dimensional scaling of the module eigengene vectors. Modules are color coded based on names assigned by WGCNA. Size of dots indicate number of genes in each module. Each module is labelled based on the most significant biological process category gene ontology enrichment determined by DAVID, however this label is not always all encompassing. See Online Table VIII for exhaustive list. Modules are grouped based on related functional category enrichments and distance in MDS space. D. Trajectories of expression based on eigenvectors reported by WGCNA for each module across the developmental series. Groups and color coding are the same as in C. Group 1 modules have generally declining expression and include many genes involved in developmental patterning. Group 3 modules generally have increasing expression. Groups 2 and 4 have multiphasic but offset expression and contain genes involved in chromatin regulation and muscle cell differentiation and function.
