Figure 2.
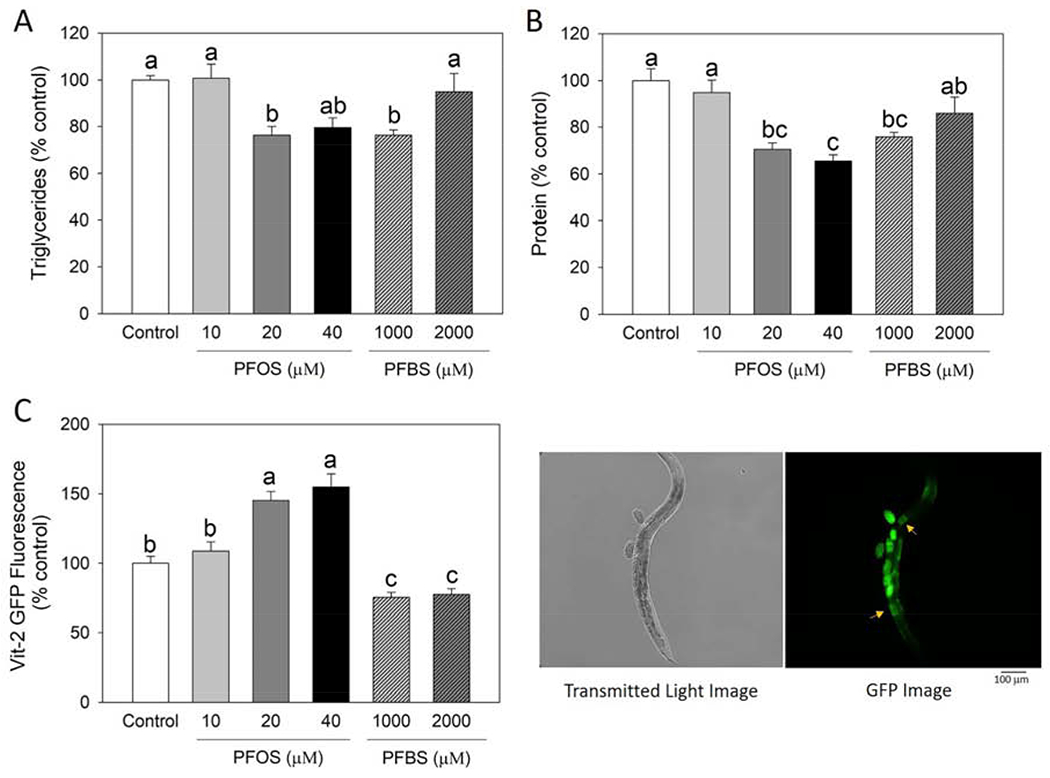
PFOS and PFBS altered the nutrient loading and nutrient composition of embryos. Synchronized L4/young adult worms were treated with control (0.1% DMSO) or PFOS or PFBS for 2 days at 20°C, then eggs were collected by bleaching method. Embryonic triglyceride (A) and protein (B) contents were measured and normalized by DNA concentration. Results are expressed as mean±S.E (n=4 plates, each plate contained >5,000 nematodes). (C) Effect of PFOS and PFBS on embryonic yolk uptake. Nutrient loading was monitored by quantifying the yolk uptake into oocytes with transgenic C. elegans strain DH1033. Synchronized L4/young adult DH1033 worms were treated for 1 day at 20°C. After treatment, worms were randomly selected for the fluorescence analysis. VIT-2::GFP expression was analyzed by Image J software by quantifying fluorescence intensity in the first pair of mature oocytes (yellow arrows) (n=115 for control, n=85 for 10 μM PFOS, n=105 for 20 μM PFOS, n=55 for 40 μM PFOS, n=107 for 1,000 μM PFBS, and n=113 for 2,000 μM PFBS). Results represent data collected from one experiment. a,b,c Means with different letters are significantly different (P<0.05).
