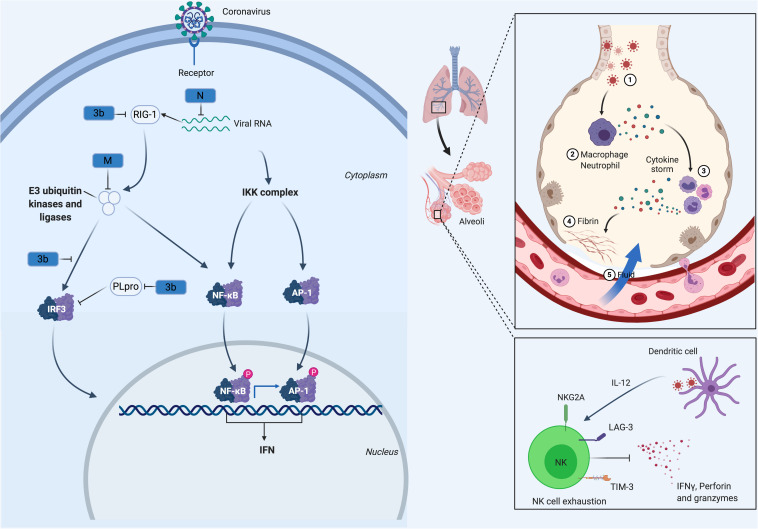
FIGURE 1.
CoV Innate Immune Evasion. The innate immune response to CoV’s is activated upon detection of viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns, such as double-stranded RNA, via host PRRs such as RIG-I. Following viral recognition, transcription factors including NF-κB, AP-1 and IRF3 are activated and translocate to the nucleus where they induce the expression of interferons. Both MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV, through their M, N, non-structural proteins (NSP1, 3b, 4a, 4b, 5, 6), and PLpro, have developed mechanisms to interfere with these signaling pathways. This alters the cytokine secretion profile of infected cells to enhance the recruitment of myeloid immune cells over NK cells, which in turn produce more cytokines, creating a cycle of inflammation that damages the lung. Many of these processes are likely conserved in SARS-CoV-2.