Fig. 1. Extinction mental context decoding.
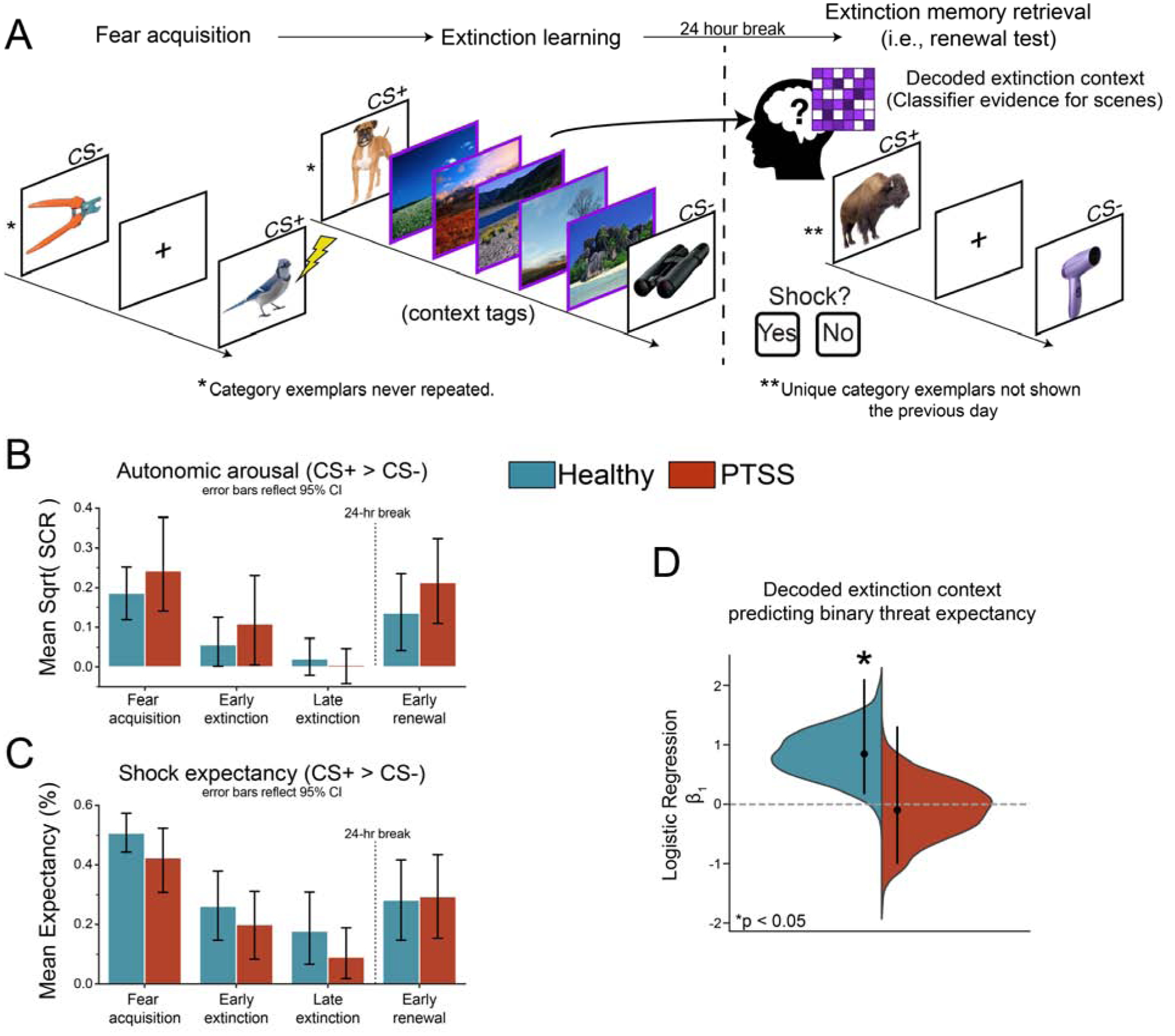
A. Experimental Design. During fear acquisition 50% of CS+ co-terminated with a mild electric shock (US). During extinction, no shocks were delivered, and the ITIs were replaced with natural scene context tags. 24 hours later, participants were placed back into the scanner and shown novel CS+/− images. MVPA classifier evidence on CS+ trials during the renewal test provided evidence for reinstatement of the mental context associated with scene images from extinction memory formation. B. Mean square root transformed differential SCR (CS+ > CS−) shows successful acquisition, extinction, and renewal for both groups. Error bars reflect 95% bootstrapped confidence intervals (N iteration = 1000). See section 3.1 and Supplementary Figures 6 & 7 for details. C. Mean differential shock expectancy (CS+ > CS−). For this analysis responses were coded as Expect a Shock = 1, Do not expect = 0, and averaged within each phase, such that higher values indicate more shock expectancy. See section 3.1 and Supplementary Figure 5 for details C. Decoded extinction mental context related to conscious threat expectancy during early extinction. Subjects responded “Yes” or “No” if they expected a shock on each trial. Error bars represent mean and one-sided 95% bootstrap CIs.
