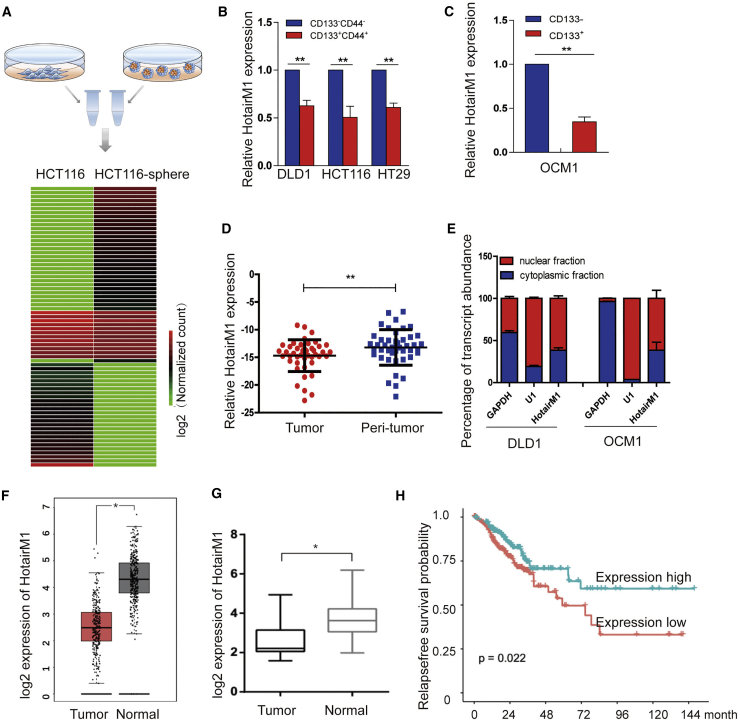
Figure 1.
HotairM1 Is Expressed at Low Levels in CSCs
(A) Workflow depicting the isolation of CSCs from the sphere formation assay using serum-free medium and differentially expressed lncRNAs from transcriptome analysis. (B) HotairM1 was detected in CD44+CD133+ colorectal cancer cells by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Data are indicated as the mean ± SD. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (C) HotairM1 was detected in CD133+ OCM1 cells by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. Data are indicated as the mean ± SD. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) HotairM1 was detected in tumor tissues and paired adjacent tumor tissues (n = 37). (E) Fractionation of tumor cells followed by quantitative real-time PCR. U1 RNA served as a positive control for nuclear gene expression. GAPDH RNA served as a positive control for cytoplasmic gene expression. N, nuclear fraction; C, cytoplasmic fraction. Data are indicated as the mean ± SD. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (F) HotairM1 expression in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) was analyzed using the GEPIA database (number of tumor cells, 275; number of normal cells, 349). (G) HotairM1 expression was analyzed using the GEO database (GEO: GSE104836). (H) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of HotairM1 using GEO: GSE104836. The cutoff value was set according to the median value of HotairM1 normalized expression. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, by two-tailed Student’s t test.