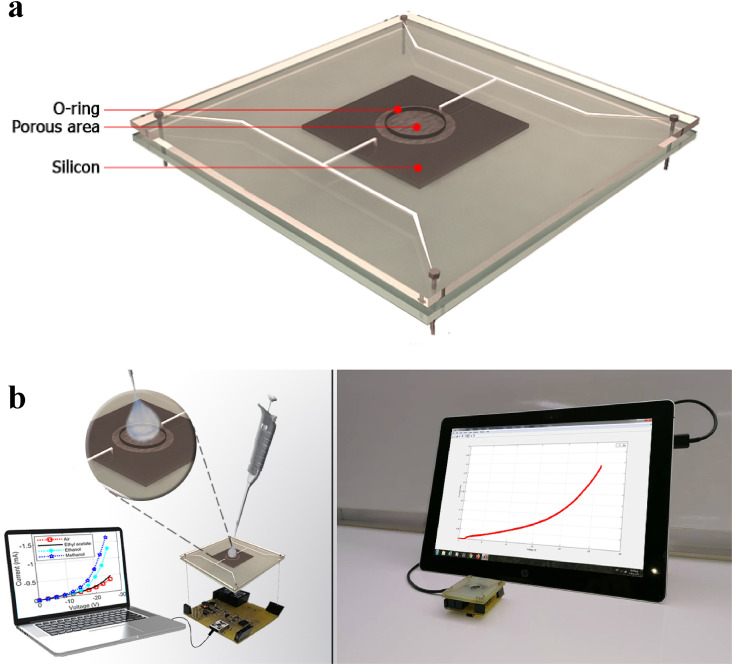
Fig. 3.
The whole device and measurement set up is presented here. The sample and its connections are shown schematically here because the actual unit, given in Fig. b, is opaque and the details cannot be seen. Two printed circuit boards push on an O-ring and sandwich the sample. Only the porous area is exposed to the liquid that is poured into the opening. The O-ring prevents the liquid from reaching other parts of the sample. Connections to the porous area and Si itself happen by pressing Ag terminals on the contacts to these areas via Silver paste. The sample holder is inserted into the measuring circuit that sends current into the device and measures its voltage. The result is sent to a computer of which the USB port is used to power the circuit itself.