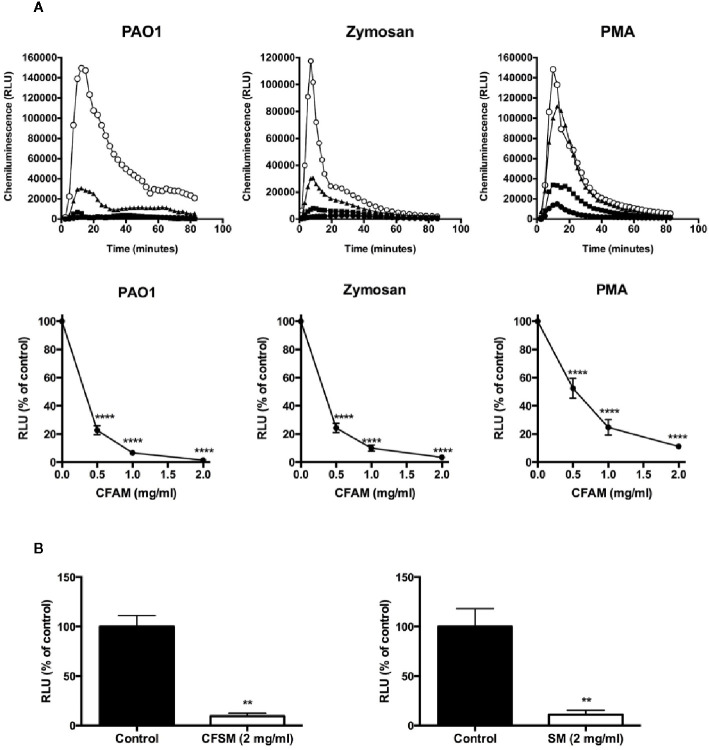
Figure 3.
Mucin suppression of intracellular chemiluminescence in neutrophils activated by opsonized PAO1 bacteria, opsonized zymosan and PMA. (A). Neutrophils isolated from the peripheral blood of healthy volunteers were incubated with opsonized PAO1 at a bacteria:neutrophil ratio of 2:1, 2.5 mg/ml of opsonized zymosan, or 1 µg/ml of PMA. Luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence in the presence of superoxide dismutase and catalase was measured over time in a luminometer. (Top row: open circles = no CFAM; triangles = CFAM, 0.5 mg/ml; squares = CFAM, 1 mg/ml; closed circles = CFAM, 2 mg/ml). The bottom row shows the mean ± sem of the maximal RFU data points recorded in repeated experiments. (n = 4 experiments, ****P < 0.001 vs. no mucin). (B) Mucins derived from the saliva of CF (CFSM) and non-CF (SM) individuals also suppressed neutrophil chemiluminescence in the presence of opsonized PAO1 bacteria (n = 3 experiments, **p < 0.01 vs. non mucin).