Figure 2.
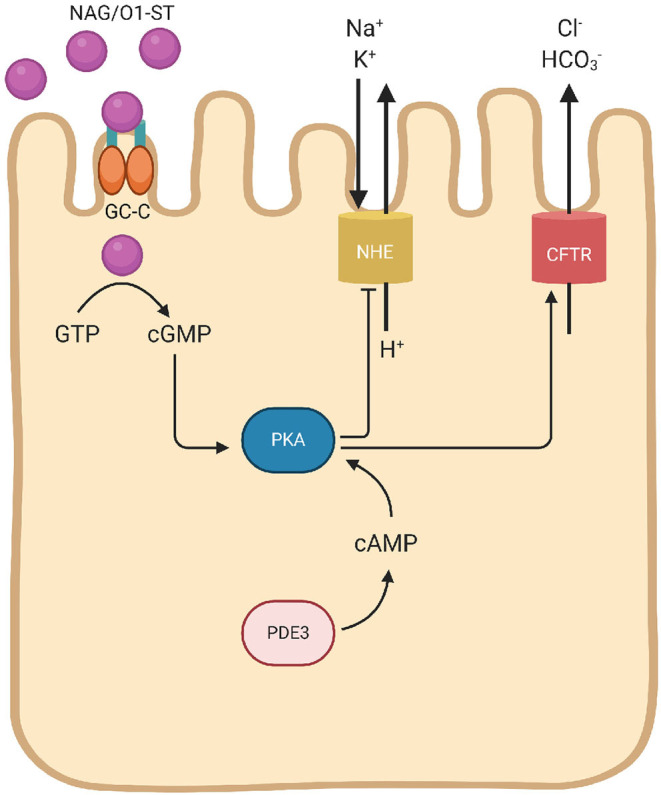
Schematic mechanisms of V. cholerae heat-stable eterotoxin (NAG/O1-ST). NAG/O1-ST bind to the intestinal guanylate cyclase (GC-C). Activation of intracellular catalytic domain of GC-C result in the formation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). This intracellular transformation activates cGMP-cAMP-dependent PKA leads to CFTR phosphorylation. cGMP reduces Na+ and Cl− absorption through the NHE, and also inhibits phosphodiesterase-3 (PDE3) leading to cellular accumulation of cAMP, and subsequent activation of PKA. Phosphorylation of the CFTR leads to secretion of Cl− with and decreased NaCl absorption, which results in diarrhea.
