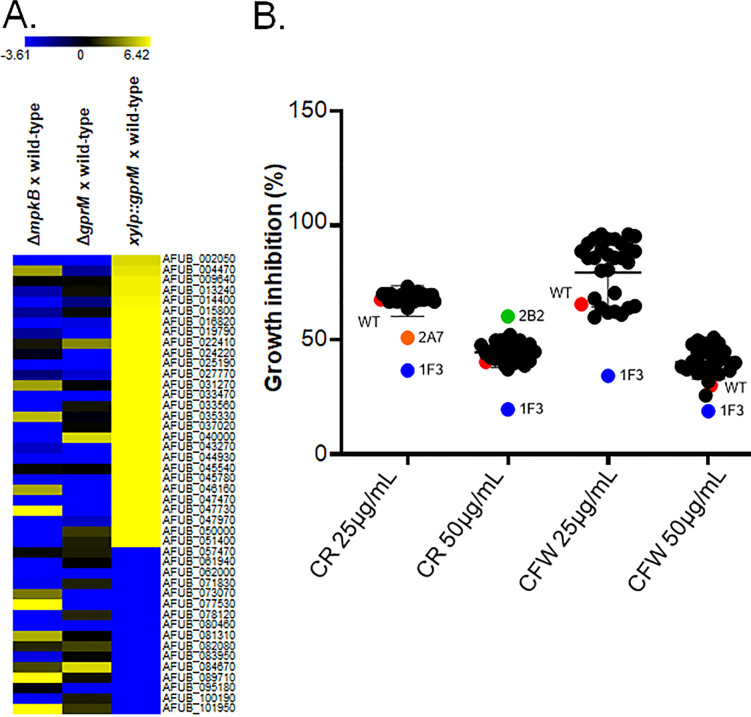
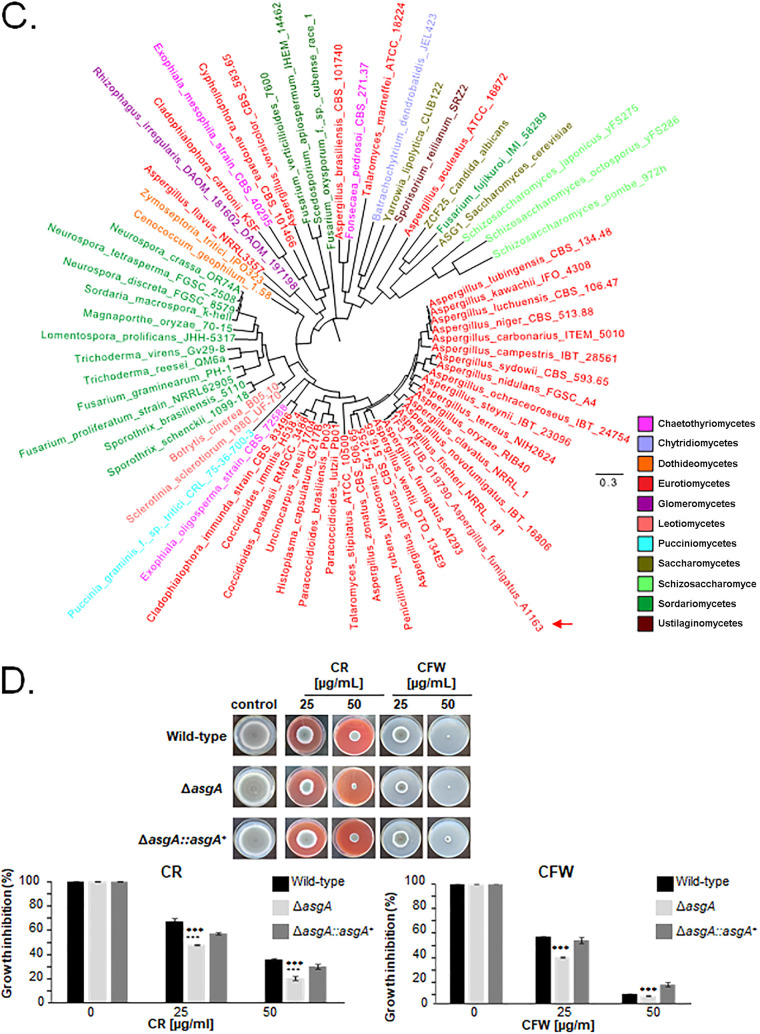
FIG 11.
Identification of a TF involved in mediating the response to cell wall damage. (A) Heat maps depicting the log2 fold change of 44 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), as determined by RNA-seq, and encoding transcription factors (TFs) that were modulated in the xylP::gprM strain. Log2FC values are based on comparisons between the mpkB and gprM deletion strains and the gprM-overexpressing (xylP::gprM) strain and the wild-type strain. Heat map scale and gene identities are indicated. Hierarchical clustering was performed in MeV (http://mev.tm4.org/), using Pearson correlation with complete linkage clustering. (B) Identification of the TF AsgA as important for cell wall stress resistance. Graph showing the percentage of growth of 44 TF deletion strains (named by simple numbers and letters) in the presence of different concentrations of the cell wall-damaging agents Congo red (CR) and calcofluor white (CFW). The growth percentage was calculated by dividing colony diameter in the presence of the drug by the colony diameter in the control, drug-free condition specific to each strain. The 1F3 strain, subsequently named ΔasgA strain, was significantly more sensitive to the cell wall-perturbing compounds. (C) The phylogenetic distribution of AsgA across fungal classes and genomes. Sequences were aligned through ClustalW implemented in Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis 7 (MEGA7) software (59). Phylogenetic analyzes were performed using the MEGA7 software, using the neighbor-joining method (60) and 1,000 bootstrap replications (61) for each analysis. The phylogenetic tree was visualized using the FigTree program (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/). The red arrow indicates the asgA gene. (D) Confirmation of AsgA-mediated sensitivity to CR and CFW. Strains were grown from 105 spores for 5 days at 37°C on glucose minimal medium supplemented with increasing concentrations of CR and CFW before pictures were taken (left) and radial diameter of biological triplicates was measured (right). Standard deviations represent the average of three biological replicates. ***, P < 0.0005 in a one-tailed, paired t test in comparison to the wild-type (WT) strain.