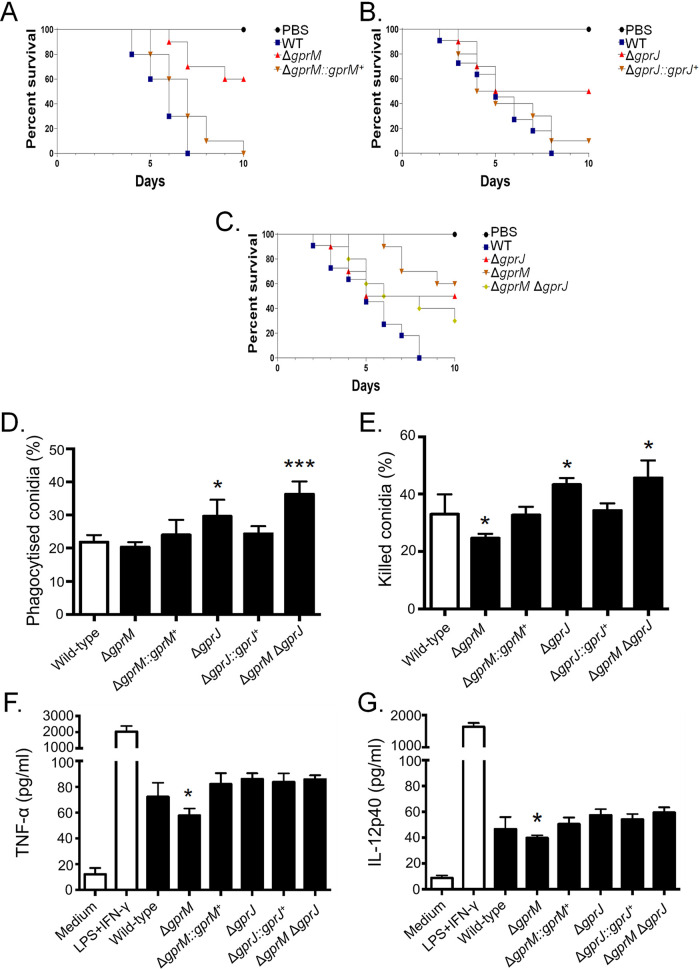
FIG 12.
GprM and GprJ are important for A. fumigatus virulence in G. mellonella wax moth. (A to C) Survival curves of G. mellonella larvae (n = 10/fungal strain) infected via injection with 106 conidia of the gprM and gprJ single- and double-deletion strains. Larval survival was monitored over a time period of 10 days. (D and E) Bone marrow-derived murine C57BL/6 macrophages (BMDMs) phagocytize (D) and kill (E) a higher number of ΔgprJ and ΔgprM ΔgprJ conidia in vitro, whereas they kill less ΔgprM conidia. (F and G) Concentrations of the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 12 (IL-12) p40 cytokines in BMDMs infected with live-resting (LR) conidia, show that ΔgprM conidia elicit a reduced inflammatory response. Positive control, lipopolysaccharide plus interferon γ (LPS + IFN-γ). Standard deviations represent the average of three biological replicates, and all the strains were compared with the wild-type and complemented strains (*, P < 0.05 in a two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test).