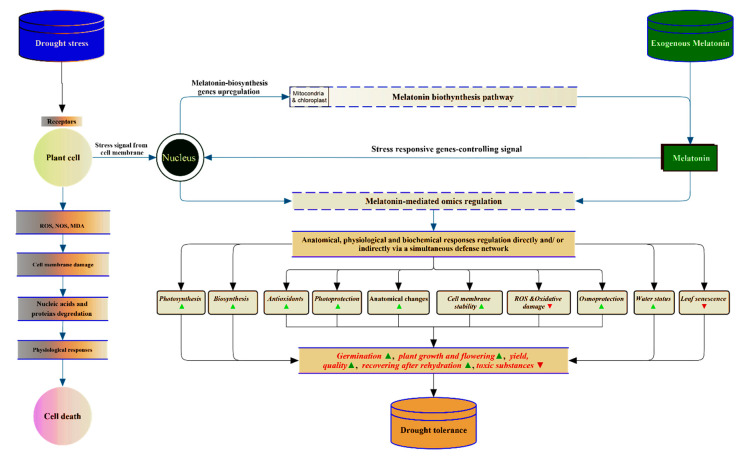
Figure 1.
A schematic model explaining the mechanism underlying the melatonin-mediated drought stress response. At the cellular level, a stress signal from the cell membrane is received by the nucleus, which starts to activate the melatonin biosynthesis pathway from its precursor, tryptophan, in mitochondria and chloroplasts by upregulating the melatonin-biosynthesis genes. Melatonin sends its feedback on such stress to the nucleus to activate omics regulation. Consequently, the genes encoding the proteins related to plant anatomical, physiological, and biochemical responses are regulated directly and/or indirectly via a simultaneous defense network. The omics-mediated responses include photosynthesis, biosynthesis, enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants, photoprotection, cell membrane stability, ROS and oxidative damage, osmoprotection, water status, and leaf senescence, in addition to the anatomical changes, which lead to drought tolerance. Consequently, the whole plant status is enhanced, including growth and development, flowering, yield, quality, and survival rate, while the toxic substances are decreased.