Figure 4.
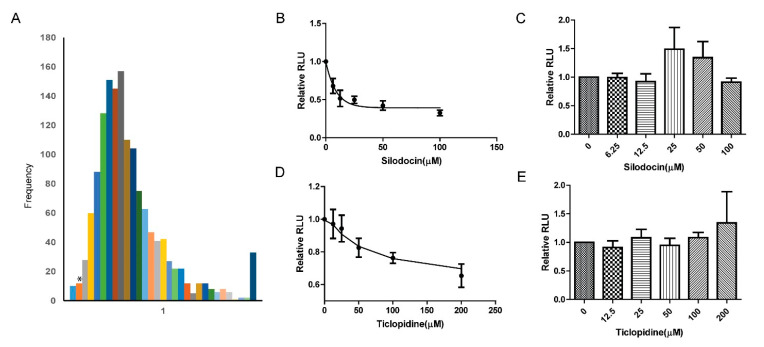
C-P4H1 inhibitors are identified with the high-throughput screening assay from the FDA-approved drug library. (A) The frequency for relative activity of P4H1 at the presence of each chemical. Over 1400 FDA-approved drugs were screening in the 384 well plate or 96-well plate at 50 µM. 50 µM DHB was used as a positive control in each plate. All the ATP signals produced by the plate reader were normalized with the equation: . *, the relative activity of C-P4H1 in the presence of DHB. (B) Silodocin inhibitory activity was analyzed at different concentrations. All the ATP signals produced by the plate reader were normalized to vehicle control, control value is 1; n = 3. (C) Silodocin did not inhibit the Succinate-GloTM Hydroxylase assay in the absence of WT-P4H1; n = 3. (D) Ticlopidine inhibitory activity was analyzed at different concentrations; 200 nM C-P4H1 in the reaction. The C-P4H1 activities in ticlopidine-treated samples were normalized with vehicle control, control value is 1; n = 3. (E) Ticlopidine did not inhibit the Succinate-GloTM Hydroxylase assay in the absence of WT-P4H1; n = 3. The data displayed as means ± standard deviation (SD).