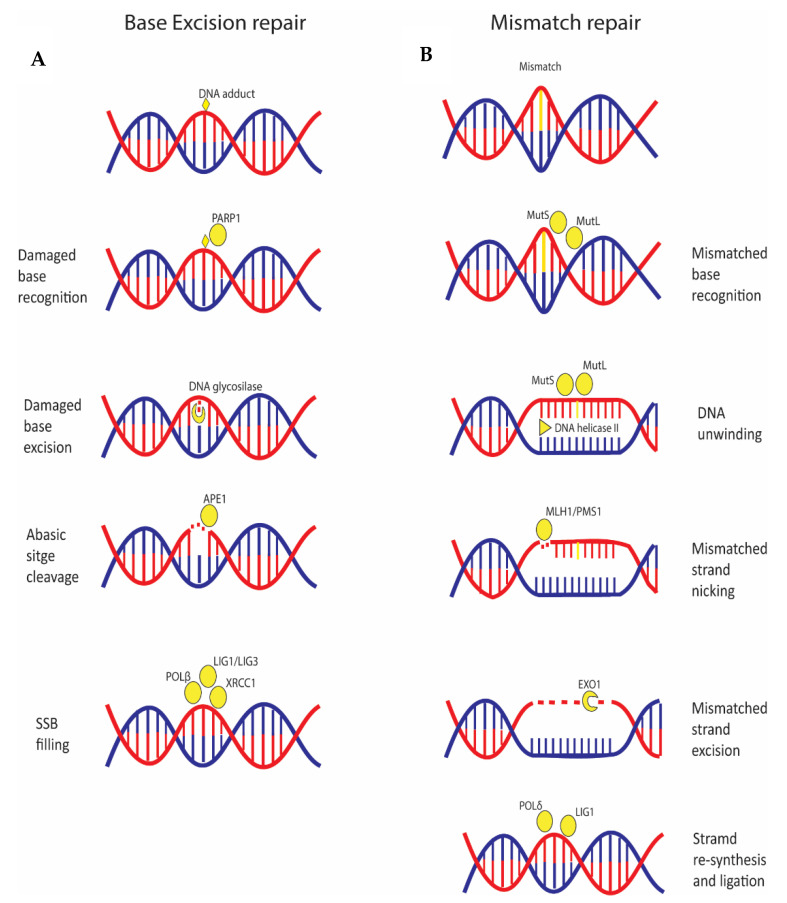
Figure 3.
Small base lesions are repaired by base excision repair; mismatched base pairs and insertion/deletion loops are corrected by mismatch repair pathway. (A) DNA lesion is recognized by PARP1 which recruits a DNA glycosylase that removes the damaged base; then, APE1 digests the abasic site determining a SSB that is repaired by the combined action of LIG1/3, XRCC1 and Pol-β. (B) The mismatched base is recognized by the complexes MutS and MutL that, in turn, recruit the DNA helicases II to unwind the DNA strands; thereafter, the complex formed by MLH1/PMS1 digests DNA several bases from the mismatch, forming a nick. The EXO1 nuclease digests the DNA from the nick towards the mismatch; finally, the removed strand is re-synthetized by Pol-δ and ligated by LIG1.