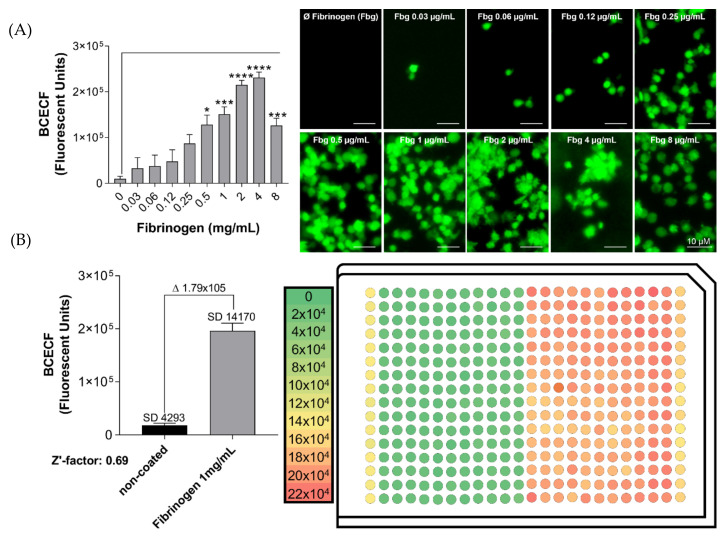
Figure 6.
Z′-factor calculation to validate the platelet adhesion assay in a 384-well microplate. (A) Platelet adhesion similarity between 96- and 384-well microplates. Coating of 384-well microplate with different concentrations of fibrinogen (Fbg 0.03 to 8 mg/mL in 20 µL), or incubation with distillated water, were performed for 1 h at 37 °C. After blocking the wells with BSA (0.03%), human washed platelets (8 × 104/µL in 10µL) were added, followed by incubation for 1 h at 37 °C. Next, non-adherent platelets were removed, and adherent platelets were incubated with BCECF-AM (4 µg/mL in 20 µL) for 30 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence intensity was measured using a plate reader (VictorX, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). Values were compared with the control condition (non-coated plastic) by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test (* p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.000,1 values presented as SEM resulting from duplicate average of four independent experiments). Images were acquired using a fluorescence microscopy (Eclipse Ti2, Nikon) with a 20x objective. (B) Z′-factor calculation to validate the platelet adhesion assay. In a 384-well microplate, 20 µL of water were added to half of the microplate (176 wells—left side). In the other half, fibrinogen (1 mg/mL) diluted in water was added (176 wells—right side). After blocking the wells with BSA (0.03%), human washed platelets (8 × 104/µL in 10 µL) were added, followed by incubation for 1 h at 37 °C. Next, non-adherent platelets were removed, and adherent platelets were incubated with BCECF-AM (4 µg/mL in 20 µL) for 30 min at 37 °C. As a control, platelet adhesion on plastic was measured in the first and last columns. Δ represents delta: (Fibrinogen) − (non-coated). Fluorescence intensity (F.I.) was measured using a plate reader (VictorX, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The data of the graphs showing the Z′-factor were calculated using the equation previously published by Zhang et al. [22].