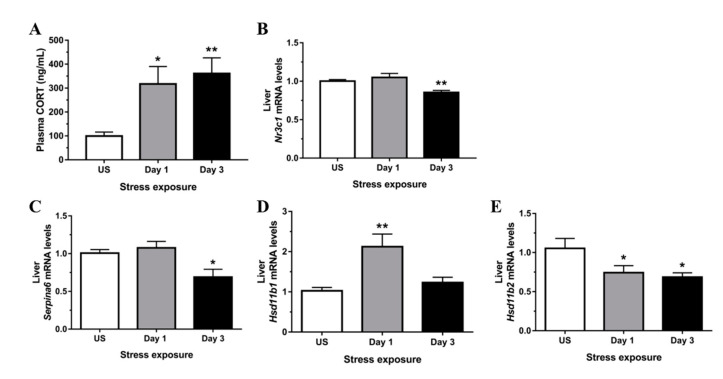
Figure 1.
Restraint stress (A) increases circulating corticosterone (CORT), (B) reduces expression of glucocorticoid receptor (Nr3c1) and modulates mRNA expression of hepatic mediators of glucocorticoid bioavailability including (C) corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG; Serpina6), (D) hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase 1 (Hsd11b1), and (E) hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase 2 (Hsd11b2) compared to unstressed (US) rats (n = 6–8/group). Results in (C,E) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD test; (A,B,D) were analyzed using non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.