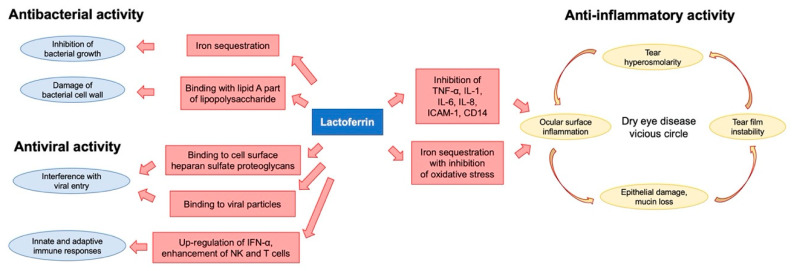
Figure 1.
Flowchart showing the mechanisms of action of lactoferrin in ocular diseases. Iron sequestration is the basis of the bacteriostatic effect of lactoferrin. The molecule also has a direct bactericidal activity thanks to its binding with lipid A domains of the bacterial lipopolysaccharide. The binding to viral surface components as well as to heparansulfate proteoglycans inhibits the virus–host cell interaction and is responsible for the antiviral activity. Moreover, lactoferrin regulates innate and adaptive immune responses against infections. The effects of lactoferrin on the vicious circle of dry eye disease are related to the downregulation of numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as to the anti-oxidative activity.