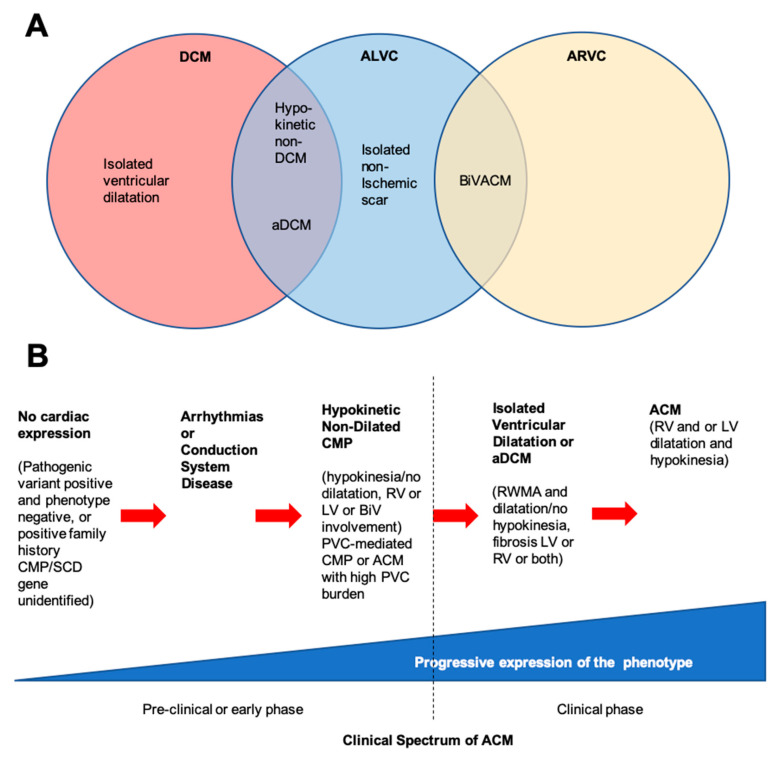
Figure 2.
Spectrum of clinical presentations of right ventricular disease, left ventricular disease, and dilated cardiomyopathy. (A) ACM and ALVC show overlapping phenotypes with ARVC, but the pathology is seen primarily in the left ventricle (although right ventricle is also usually affected). (B) Timeline showing the clinical features of ACM. Hypokinetic non-dilated cardiomyopathy and isolated-ischaemic scar pertain to the pathology where there is marked ventricular scarring as identified by cardiac MRI. Modified from Elliott et al. (2019) [22] and Pinto et al. (2016) [24]. ACM = arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; aDCM = arrhythmogenic dilated cardiomyopathy; ALVC = arrhythmogenic left ventricular cardiomyopathy; ARVC = arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy; BiV = biventricular; BivACM = biventricular arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; CMP = cardiomyopathy; DCM = dilated cardiomyopathy; LV = left ventricle; PVC = premature ventricular contraction; RV = right ventricle; RWMA = regional wall motion abnormality; SCD = sudden cardiac death.