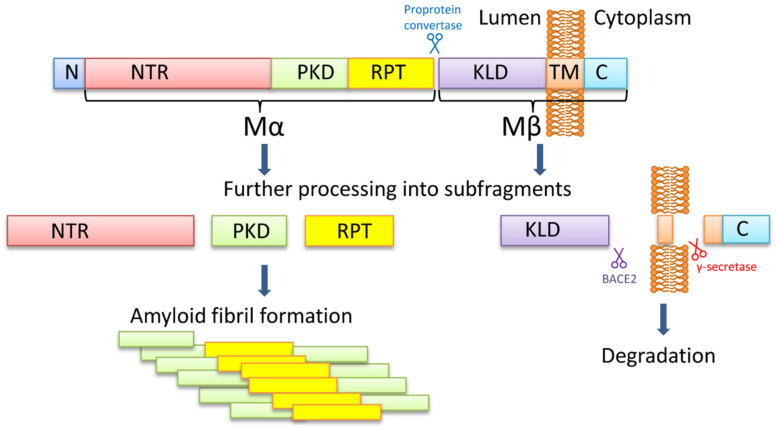
Figure 1.
The PMEL17 processing and formation of amyloid fibrils. The PMEL17 is cut in endoplasmic reticulum and then transported to Golgi apparatus for O-glycosylation. Later in the acidic environment of premelanosomes, the proprotein convertase cuts it to the Mα (an N-terminal ectodomain) and the Mβ (the C-terminal polypeptide containing the transmembrane domain) fragments. The fragments remain connected via the disulfide bond. The BACE2 cuts the Mβ fragment out of the membrane, and so the Mα with the attached KLD domain becomes luminal. Serial cleavages later process the Mα fragment into subfragments, which can create amyloid fibrils in premelanosome. NTR—N-terminal region; PKD—polycystic kidney disease domain; RPT—proline, serine, threonine-rich repeat domain; KLD—kringle-like domain; TM—transmembrane domain; C—cytoplasmic domain.