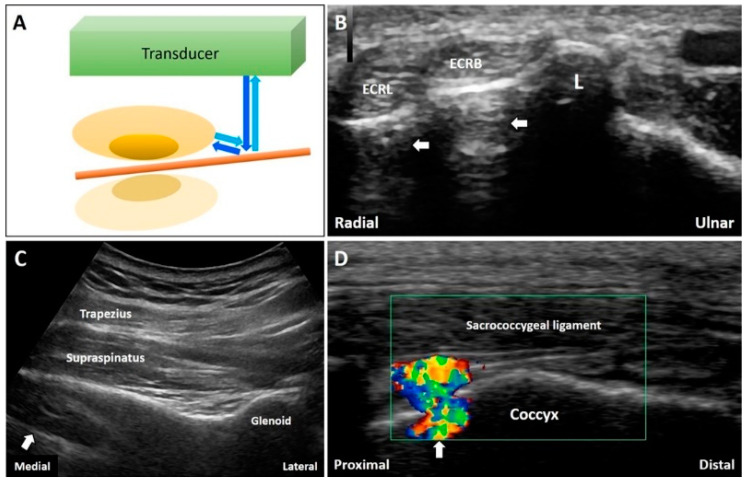
Figure 9.
When the sound waves encounter a reflective interface, the reflected beam would cast a mirror image at the opposite side of the interface (A). The mirror artifacts can be seen at many body regions like the forearm (B), supraspinatus fossa (C), and coccyx (D). White arrow: mirror artifact. ECRL: extensor carpi radialis longus tendon; ECRB: extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon; L: Lister’s tubercle Blue arrows: the projected and reflected US beams. Brown pillar: the reflective interface. Green box: the color box for detection of Doppler signals.