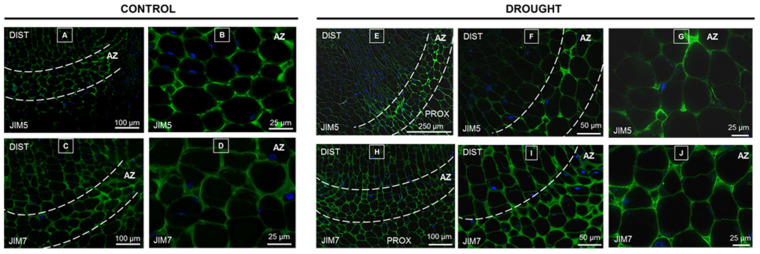
Figure 4.
Drought leads to redistribution of low- and high-methylated pectin in the abscission zone (AZ) area. Immunolocalization of pectin in the flower AZ of yellow lupine cultivated under soil drought conditions (25% WHC, water deficit conditions) (E–J) and AZ of control lupines growing in the soil of optimal moisture (70% WHC) (A–D). For analysis, sections of AZs (marked by the white dotted line) were collected on the 48th day of cultivation. Low-methylated and un-methylated homogalacturonans (HGs) were detected by JIM5-Ab, while JIM7-Ab was used to localize high-methylated HGs. Green fluorescence indicates the pectin presence, while the blue signal corresponds to nuclei stained with DAPI. Images (B,D) are magnifications of AZ areas presented in (A,C), respectively. Images (F,G) are magnified regions presented in (E). Images (I,J) are magnified regions presented in (H). Abbreviations: DIST—distal region, flower pedicel fragment above the AZ; PROX—proximal region, stem fragment below the AZ. Bars are given on each image.