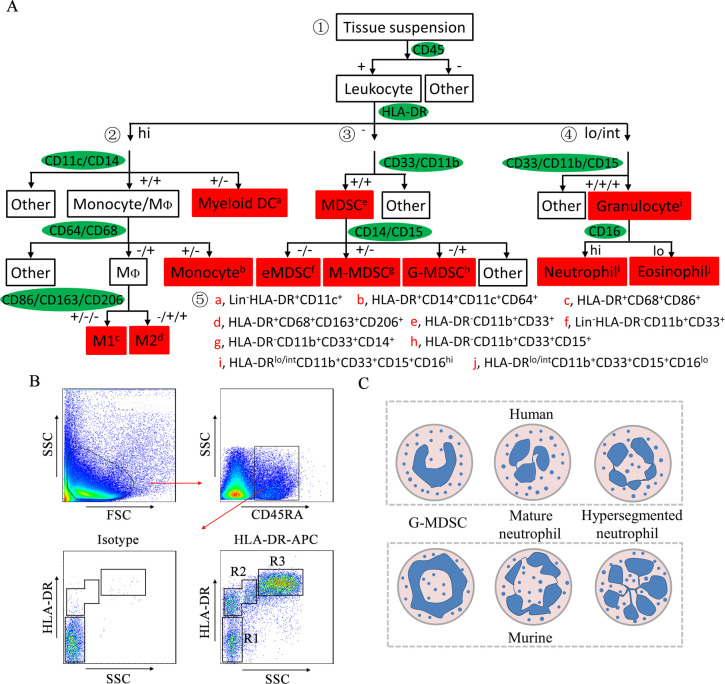
Figure 1.
Strategy for the identification of human colorectal-infiltrating MDSCs. (A) Gating strategy of colorectal-infiltrating myeloid cells. ① Leukocytes are divided into three groups based on HLA-DR levels. ② Monocytes/MΦs and DCs are distinguished from HLA-DRhi cells based on the expression of CD11c and CD14. M1 and M2 macrophages are distinguished based on the expression of CD86, CD163, and CD206. ③ MDSCs are distinguished from HLA-DR− cells based on the expression of CD33 and CD11b. eMDSCs, M-MDSCs and G-MDSCs are distinguished based on the expression of CD14 and CD15. ④ Granulocytes are distinguished from HLA-DRlo/int cells based on the expression of CD33, CD11b, and CD15. Neutrophils and eosinophils are distinguished based on the expression of CD16. ⑤ Immunophenotypes of human colorectal-infiltrating myeloid cells. (B) Representative FACS plots of leukocytes based on HLA-DR levels. Leukocytes were isolated from the CRC tissue suspension by CD45RA and then divided into three groups based on HLA-DR levels. R1: HLA-DR− cells; R2: HLA-DRlo/int cells; R3: HLA-DRhi cells. (C) Schematic representations of the nuclear morphology of G-MDSCs and neutrophils. APC, allophycocyanin; DC, dendritic cell; eMDSC, early-stage myeloid-derived suppressor cell; FACS, flow cytometry; FSC, forward scatter; G-MDSC, granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen DR; MΦ, macrophage; M1, M1 macrophage; M2, M2 macrophage; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; M-MDSC, monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell; SSC, side scatter.