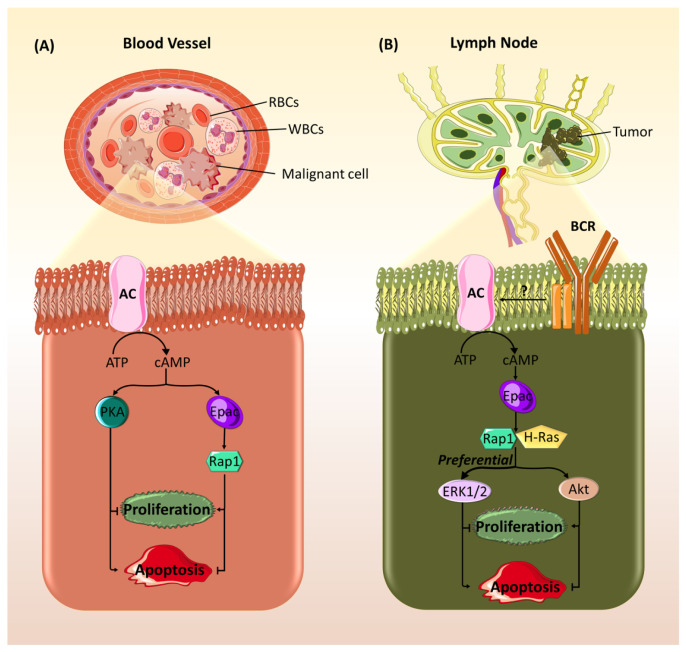
Figure 4.
Epac has opposing effects on cell proliferation and apoptosis in different blood cancers types. (A) Epac enhances cell growth and survival and inhibits apoptosis in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. cAMP can act through both downstream effectors, Epac and protein kinase A (PKA), that have contradictory effects. In contrast to PKA, Epac, through Rap1, plays an anti-apoptotic role and elicits pro-survival effects. (B) Epac promotes cell growth arrest and apoptosis in immature B cell lymphoma. Activation of B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) leads to activation of AC and a subsequent accumulation of cAMP. cAMP in its turn activates Epac, which acts through the small G proteins, Rap1 and H-Ras, to activate the pro-apoptotic ERK1/2 and the anti-apoptotic Akt. This activation seems to be more preferential towards ERK leading to a final result of growth arrest and increased apoptosis.