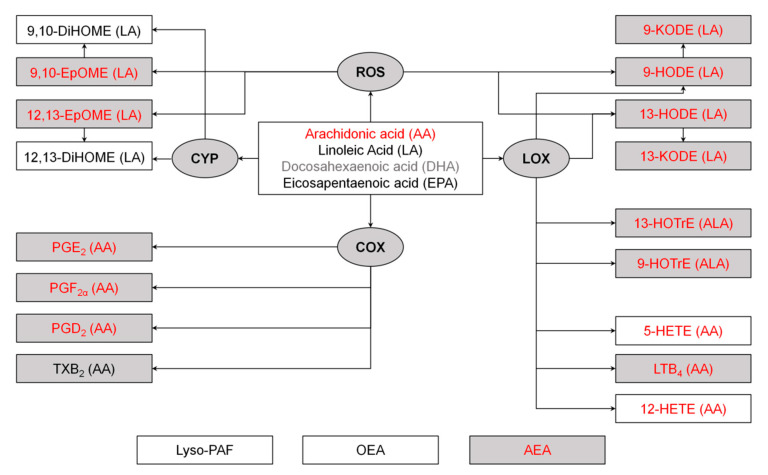
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of biosynthesis of lipid mediators. Metabolites of arachidonic acid (AA), linoleic acid (LA) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) are divided into the groups synthesized via lipoxygenase (LOX), cyclooxygenas (COX), cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (CYP) or reactive oxygen species (ROS) dependent pathways. The other abbreviations are as follows: AEA, N-arachidonoylethanolamine; DHA, docosahexaenoic acids; 9,10-DiHOME, 9,10-dihydroxyoctadecamonoenoic acid; 12,13-DiHOME, 12,13-dihydroxyoctadecamonoenoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; 9,10-EpOME, 9,10-epoxyoctadecamonoenoic acid; 12,13-EpOME, 12,13-epoxyoctadecamonoenoic acid; 9-HODE, 9-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid; 13-HODE, 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid; 9-KODE, 9-oxo-octadecadienoic acid; 13-KODE, 13-oxo-octadecadienoic acid; LTB4, leukotriene B4; lyso-PAF, lyso-platelet-activating factor; OEA, oleoylethanolamine; PGD2, prostaglandin D2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PGF2α, prostaglandin F2α. The mediators altered in DES and affected by the proposed anti-inflammatory therapy (see below) are indicated in red and gray colors, respectively.