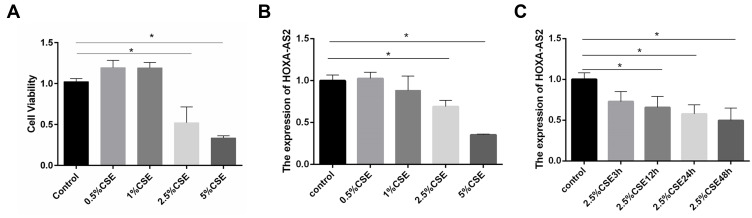
Figure 3.
CSE treatment inhibited the proliferation of HPMECs and reduced HOXA-AS2 expression. (A) HPMECs were treated with different concentrations of CSE, including 0, 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.5%, and 5.0% for 24 h, and the proliferation of HPMECs was measured by CCK-8 assay. (B) HPMECs was exposed to CSE of different concentrations (0, 0.5%, 1.0%, 2.5%, and 5.0%) for 24 h, and the relative expression levels of HOXA-AS2 was measured by real-time-PCR. At the concentrations of 2.5% and 5% CSE, the cell viability decreased significantly. (C) HPMECs were treated with 2.5% CSE for different amounts of time, and the relative expression levels of HOXA-AS2 were measured by real-time PCR. The expression of HOXA-AS2 decreased significantly as the treatment time extended. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. We used GAPDH as the internal loading control and calculated the relative expression of lncRNA by 2−∆∆CT method. All experiments were performed independently at least 3 times.
Abbreviations: CSE, cigarette smoke extract; real-time PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction; HPMECs, human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells; CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8.