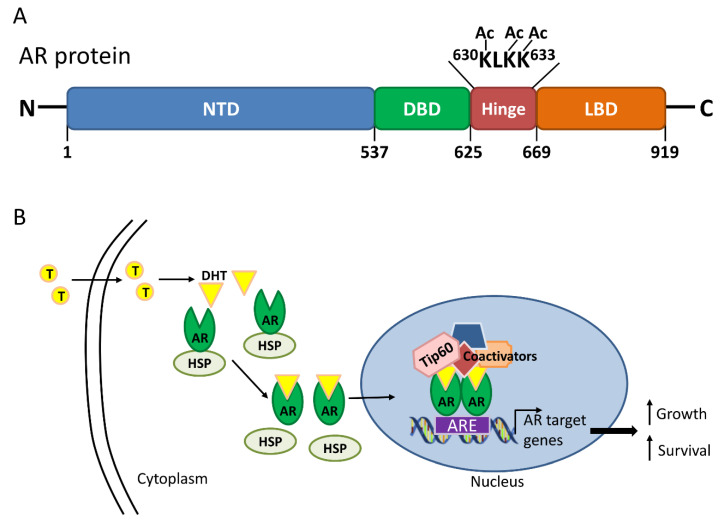
Figure 2.
Androgen receptor (AR) structure and activation in the presence of androgen. (A) The AR consists of 919 amino acids with four distinct domains, including the N-terminal domain (NTD), DNA-binding domain (DBD), hinge and ligand-binding domain (LBD). Direct acetylation (Ac) by histone acetyltransferases, including Tat interactive protein 60 kDa (Tip60), on the lysine residues of the KLKK motif within the hinge domain is critical for AR activation; (B) Upon binding of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the metabolized form of testosterone (T), the AR dissociates from the heat shock protein (HSP), translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes and binds to the androgen response element (ARE) on AR target genes. Other coactivators, including Tip60, are also recruited for the transcription of AR target genes to sustain cell growth and proliferation.