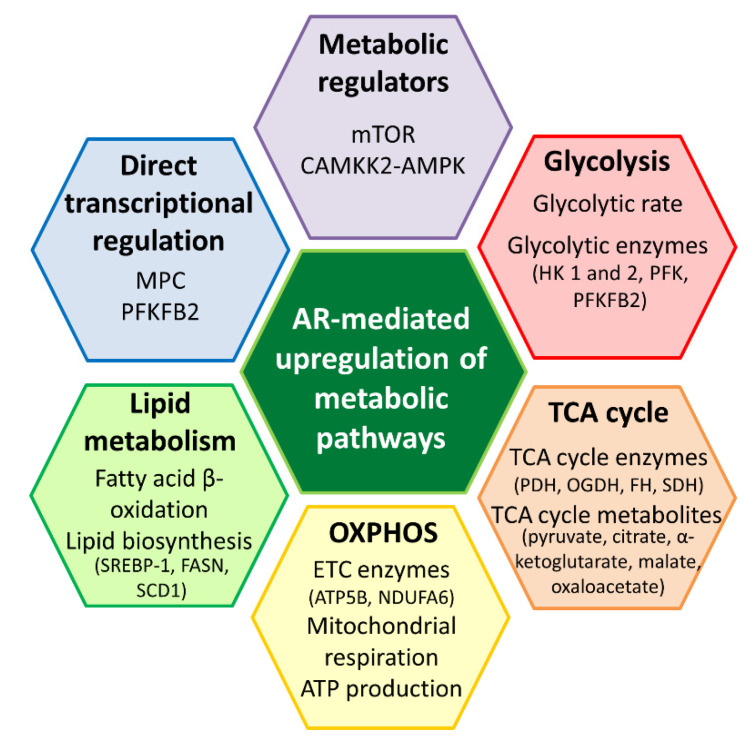
Figure 3.
Metabolic roles mediated by the androgen receptor (AR) in prostate cancer. The AR upregulates various metabolic pathways to promote the survival of prostate cancer cells. It is likely that the AR modulates metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and lipid metabolism through key metabolic regulators, including mTOR and CAMKK2-AMPK. The AR could also regulate metabolic enzyme and transporter, such as PFKFB2 and MPC through direct transcriptional regulation. AR is an important metabolic regulator in prostate cancer. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ATP5B, ATP synthase subunit beta; CAMKK2, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase 2; FASN, fatty acid synthase; FH, fumarate hydratase; HK, hexokinase; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NDUFA6, NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone); OGDH, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PFKFB2, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; SREBP-1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1.